The journey of CSS preparation starts with CSS Syllabus. Without a Syllabus, no exam exists in the world. It may be short or long, but it is necessary to provide a basic idea of content to the candidates or aspirants. CSS Syllabus provides not only an idea of the subject but it also enables students to make a good subject selection which ultimately impacts their recruitment. So, when a person harps on the journey of CSS, the very first step he/she takes is to have CSS Syllabus. Based on CSS Syllabus he makes selection and based on Syllabus he continues his/her preparation.
So, here we have given the CSS Syllabus
CSS Compulsory Subjects Syllabus:
When it comes to compulsory subjects in CSS, there are 6 subjects which as the name suggests are compulsory and everyone who chooses to sit in CSS Exam has to appear in. These are English Essay, English Precis & Composition, Pakistan Affairs, General Science & Ability, Current Affairs, Islamic Studies and Ethics (for Non-Muslims if they don’t want to choose Islamic Studies). All subjects carry equal marks i.e 100 marks. Except English Essay, every other subject has 20 marks for objective part. And excepting Islamic studies every other subject needs to be attempted in English. In, Islamic Studies, however, there is choice of attempting in URDU.
Essay Syllabus:
CSS Essay Syllabus is short but very comprehensive. The Syllabus says that in essay paper candidates will be required to write one or more Essay in English. A wide choice of topics will be given.
Candidates are expected to reflect comprehensive and research based knowledge on a selected topic. Candidate’s articulation, expression and technical treatment of the style of English Essay writing will be examined.
Click here View CSS Essay Syllabus Separately
Download CSS Essay Syllabus Pdf
English Precis & Composition Syllabus:
The examination in this subject will be based upon a paper carrying 100 marks to Test the candidate’s abilities to handle Precis Writing, Reading Comprehension, Sentence Structuring, Translation, Grammar and Vocabulary, etc.
I. Precis Writing (20 marks)
A careful selected passage with an orientation of generic understanding and enough flexibility for compression shall be given for précising and suggesting an appropriate title. Out of the total 20 marks allocated to this question, 15 shall go to précising the text and 5 to suggesting the title.
II. Reading Comprehension (20 marks)
A carefully selected passage that is rich in substance but not very technical or discipline- specific shall be given, followed by five questions, each carrying 4 marks.
III. Grammar and Vocabulary (20 marks)
Correct usage of Tense, Articles, Prepositions, Conjunctions, Punctuation, Phrasal Verbs, Synonyms and Antonyms etc.
IV. Sentence Correction (10 marks)
The sentences shall be given each having a clear structural flaw in terms of grammar or punctuation. The candidates shall be asked to rewrite them with really needed correction only, without making unnecessary alterations. No two or more sentence should have exactly the same problem, and 2-3 sentences shall be based on correction of punctuation marks.
V. Grouping of Words (10 marks)
A random list of twenty words of moderate standard (neither very easy nor utterly unfamiliar) shall be given, to be grouped by the candidates in pairs of those having similar or opposite meaning, as may be clearly directed in the question.
VI. Pairs of Words (10 marks)
Ten pairs shall be given of seemingly similar words with different meanings, generally confused in communication, for bringing out the difference in meaning of any five of them by first explaining them in parenthesis and then using them in sentences.
VII. Translation (10 marks)
Ten short Urdu sentences involving structural composition, significant terms and figurative/idiomatic expressions shall be given, to be accurately translated into English.
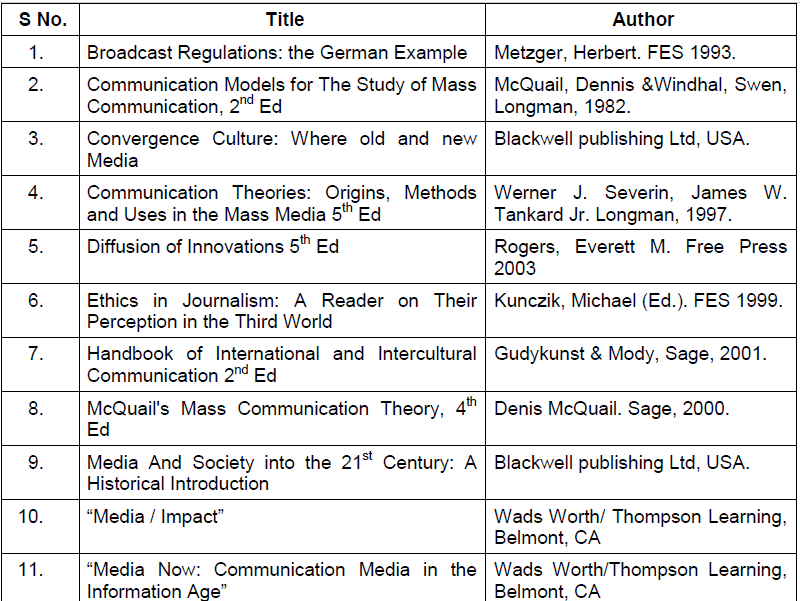
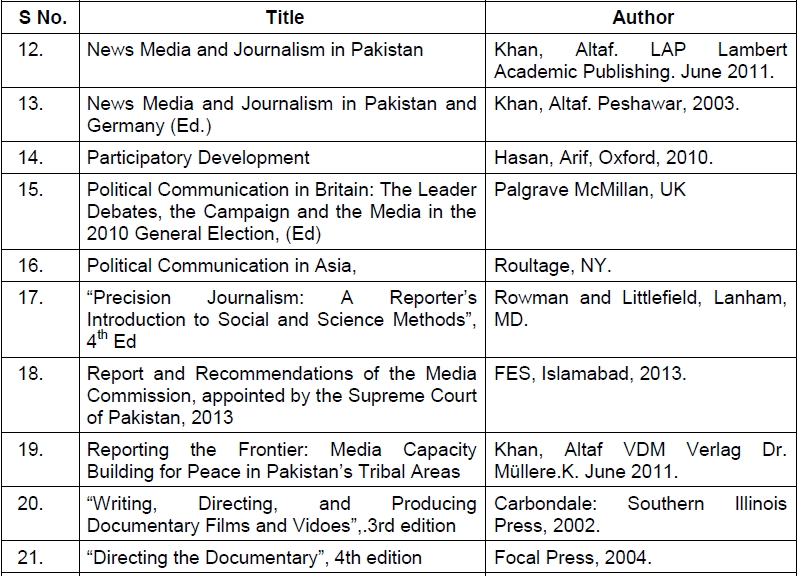
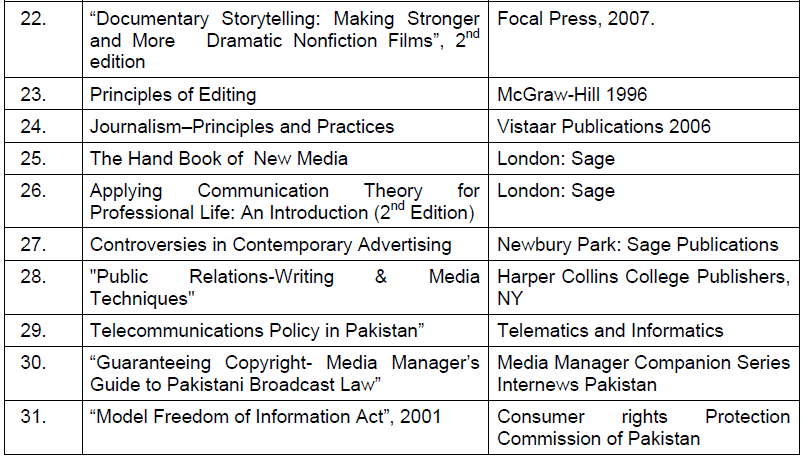
Suggested Readings
| S.No. | Title | Author |
| 1. | English Grammar in Use | Raymond Murphy (Cambridge University Press). |
| 2. | Practical English Usage | M.Swan (Oxford University Press). |
| 3. | The Little, Brown Handbook | H. Ramsey Flower & Jane Aaron (The Little, Brown & Co; Harper Collins.) |
| 4. | A University English Grammar | R. Quirk & S. Greenbaum (ELBS; Longmans) |
| 5. | Write Better, Speak Better | Readers Digest Association. |
| 6. | Modern English in Action | Henry Christ (D.C. Heath & Co.) |
Pakistan Affairs Syllabus:
Ideology of Pakistan—–definition and elucidation, historical aspects: Muslim rule in the Sub-Continent, its downfall and efforts for Renaissance. Movements for reforms– Shaikh Ahmad Sarhindi, Shah Waliullah, Sayyid Ahmad Shaheed, Aligarh, Deoband, Nadwah, and other educational institutions——-Sindh Madrassah and Islamia College Peshawae. Ideology of Pakistan in the light of Speeches and statements of Allama Iqbal and Quaid- i Azam Muhammad Ali Jinnah.
II. Land and people of Pakistan——- Geography, Society, Natural resources, Agriculture, Industry and education with reference to characteristics, trends and problems.
III. Pakistan and Changing Regional Apparatus
IV. Nuclear Program of Pakistan, its Safety and Security; International Concerns V. Regional Economic Cooperation (SAARC,ECO,SCO) and the Role of Pakistan VI. Civil-Military Relations in Pakistan
VII. Economic Challenges in Pakistan
VIII. Non-Traditional Security Threats in Pakistan: Role of Non-State Actors
IX. Pakistan’s Role in the Region
X. Palestine Issue
XI. Changing Security Dynamics for Pakistan: Challenges to National Security of
Pakistan
XII. Political Evolution Since 1971
XIII. Pakistan and US War on Terror
XIV. Foreign Policy of Pakistan Post 9/11
XV. Evolution of Democratic System in Pakistan
XVI. Ethnic Issues and National Integration
XVII. Hydro Politics ; Water Issues in Domestic and Regional Context
XVIII. Pakistan’s National Interest
XIX. Challenges to Sovereignty
XX. Pakistan’s Energy Problems and their Effects
XXI. Pakistan’s Relations with Neighbors excluding India
XXII. Pakistan and India Relations Since 1947
XXIII. Kashmir Issue
XXIV. The war in Afghanistan since 1979 and its impact on, and challenges to Pakistan, in the Post 2014 era.
XXV. Proxy Wars: Role of External Elements
XXVI. Economic Conditions of Pakistan, the Most Recent Economic Survey, the Previous and Current Budgets, and the Problems and Performance of Major Sectors of Economy.
XXVII. The Recent Constitutional and Legal Debates, the Latest Constitutional Amendments and Important Legislations, Legal Cases and the Role of Higher Courts.
XXVIII. The Prevailing Social Problems of Pakistan and the Strategies to Deal with Them, Poverty, Education, Health and Sanitation.
SUGGESTED READINGS
S.No. Title Author 1. Federalism and Ethnic Conflict
Regulation in India and Pakistan.Adeney, Katharine. , New York: Palgrave
Macmillan, 2007.2. Labor, Democratization and
Development in India and Pakistan.Candland, Christopher,
New York: Routledge, 2007.3. Perception, Politics and Security in
South Asia: The Compound Crisis in
1990.Chari, P.R. at al, New York: Routledge,
2003.4. The Future of Pakistan. Cohen Stephen P. et al. Washington: Brookings Institute Press, 2011. 5. Frontline Pakistan: The Struggle with
Militant Islam.Hussian, Zahid. New York: I.B.Tauris,
2007.6. Modern South Asia: History, Culture, Political Economy. Jalal, Aisha and Bose, Sugata. New York: Routledge, 1998. 7. Democracy and Authoritarianism in South
Asia.Jalal, Aisha, Cambridge: Cambridge
University Press, 1995.8. Conflict Between India and Pakistan: an
Encyclopedia.Lyon, Peter. California: ABC-CLIO,
2008.9. Back to Pakistan: A Fifty Year Journey. M**** Leslie Noyes. Plymouth: Rowman
& Littlefield Publishers, 2011.10. Judging the State: Courts and
Constitutional Politics in Pakistan.Newberg, Paula R. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1995. 11. Pakistan: Manifest Destiny. Qureshi, Atiff. London: Epic Press, 2009. 12. Pakistan, America, and the Future of
Global Jihad.Riedel, Bruce. Deadly Embrace: Washington: Brookings Institute Press,
2011.13. Kashmir in Conflict: India, Pakistan and the Unending War. Schofield, Victoria.
New York: I.B.Tauria, 2003.14. Islamic Law and the Law of Armed Conflict: The Armed Conflict in Pakistan. Shah, Niaz A. New York: Routledge,
2011.15. Making Sense of Pakistan. Shaikh, Farzana. New York: Colombia
University Press, 2009.16. A Brief History of Pakistan. Wynbrandt, James.
New York: Infobase Publishing, 2009.
17. Powering Pakistan: Meetings Pakistan
Energy Needs in 21st CenturyRobert M. Hathaway and Michael
Gugelman18. Pakistan’s Energy Sector: From Crisis to
Crisis-Breaking the ChainZaid Alahdad
General Science & Ability Syllabus:
Part-I (General Science) 60 Marks
· Constituents and Structure:-Universe, Galaxy, Light Year, Solar System, Sun, Earth, Astronomical System of Units.
· Process of Nature: – Solar and Lunar Eclipses, Rotation and Revolution, Weather Variables (Global Temperature, Pressure, Circulation, Precipitation, Humidity) and Weather Variations.
· Natural Hazards and Disasters: – Earth Quake, Volcanic Eruption, Tsunami, Floods, Avalanche, Travelling Cyclone (Tropical Cyclone, Middle Latitude Cyclone and Tornadoes), Drought, Wildfire, Urban Fire. Disaster Risk Management.
· Energy Resources: – Sources of Energy (Renewable i.e. LED Energy, Solar Energy, Wind Energy and Non-Renewable Energy conservation and its sustainable use.
· Atomic Structure, Chemical Bonding, Electromagnetic Radiations.
· Modern Materials/Chemicals: – Ceramics, Plastics, Semiconductors. Antibiotics, Vaccines, Fertilizers, Pesticides.
II. Biological Sciences
· The Basis of Life: – Cell Structures and Functions (Subcellular Organelles such as Nucleus, Mitochondria and Ribosomes).
· Biomolecules: – Proteins, Lipids, Carbohydrates and Enzymes.
· Plant and Animal Kingdom: – A brief survey of plant and animal kingdom to pinpoint similarities and diversities in nature.
· A Brief Account of Human Physiology.
· Common Diseases and Epidemics: – Polio, Diarrhea, Malaria, Hepatitis, Dengue their Causes and Prevention.
· New Model Concept of Producing BIO Fuel Method
III. Environmental Science
· Environment: – The Atmosphere (Layered Structure and Composition), Hydrosphere (Water Cycle, Major Water Compartments), Biosphere (Major Biomes) and Lithosphere (Minerals and Rocks, Rock Types, Plate Tectonics).
· Atmospheric Pollution: – Types, Sources, Causes and effects of major air pollutants (COx, Particulate Matter, NOx, SOx, Tropospheric Ozone, Volatile Organic Compounds, Dioxins). Regional and Global air pollution issues (Acid-rain, Ozone Depletion, Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming). International agreements on air pollution control (Montreal Protocol and Kyoto Protocol).
· Water Pollution:- Types, sources, causes and effects of major water pollutants (Synthetic Organic Chemicals, Oxygen Demanding Wastes, Plant Nutrients, Thermal Pollution, Infectious Agents, Sediments, Radioactivity, Heavy Metals and Acids). Drinking water quality and standards.
· Land Pollution: – Solid waste management and disposal.
· Role of Remote Sensing and GIS in Environmental Science.
· Population Planning.
IV. Food Science
· Concept of Balance Diet: – Vitamins, Carbohydrates, Protein, Fats and oil, Minerals, Fiber.
· Quality of Food:- Bioavailability of Nutrients, Appearance, Texture, Flavor, Quality of Packed and Frozen Food, Food Additives, Preservatives and Antioxidants
· Food Deterioration and its Control: – Causes of Food Deterioration, Adulteration, Food Preservation.
V. Information Technology
· Computer (Hardware & Software Fundamentals); I/O Processing and data storage, Networking & Internet Standards, Application and business Software, Social Media Websites. Information Systems. Fundamentals of artificial intelligence.
· Telecommunications: – Basics of Wireless Communication (Mobile, Satellite, Surveillance and GPS and Fiber Optic etc.
Part-II (General Ability) 40 Marks
VI. Quantitative Ability/Reasoning
· Basic Mathematical Skills.
· Concepts and ability to reasons quantitatively and solve problems in a quantitative setting.
· Basic Arithmetic, Algebra and Geometry (Average, Ratios, Rates, Percentage, Angles, Triangles, Sets, Remainders, Equations, Symbols, Rounding of Numbers
· Random Sampling
VII. Logical Reasoning and Analytical Reasoning/Ability
· Logical Reasoning includes the process of using a rational, systematic series of steps based on sound mathematical procedures and given statements to arrive at a conclusion
· Analytical Reasoning/Ability includes visualizing, articulating and solving both complex and uncomplicated problems and concepts and making decisions that are sensible based on available information, including demonstration of the ability to apply logical thinking to gathering and analyzing information.
VIII. Mental Abilities
· Mental Abilities Scales that measures specific constructs such as verbal, mechanical, numerical and social ability.
SUGGESTED READINGS
| S. No. | Title | Authors |
| 1. | Asimov’s New Guide to Science 1993 | Isaac Asimov |
| 2. | Science Restated: Physics and Chemistry for the Non-Scientist 1970 | Harold Gomes Cassidy |
| 3. | Eminent Muslim Scientists 1991 | S. Fakhre Alam Naqvi |
| 4. | Exploring Life Science 1975 | Walter A. Thurber, Robert E. Kilburn, Peter S. Howell |
| 5. | Exploring Physical Science 1977 | Walter A. Thurber, Robert E. Kilburn, Peter S. Howell |
| 6. | Principles of Animal Biology 2011 | Lancelot Hogben |
| 7. | The Impact of Science on Society 2005 | Isaac Asimov, A. S. a. N. A. S. a. |
| 8. | Fundamentals of Forensic Science 2010 | Max M. Houck, Jay A. Siegal |
| 9. | Forensic Science Fundamentals & Investigation 2008 | Anthony J. Bertino |
| 10. | Physical Geography 2013 | Harm J. de Blij, Peter O. Muller, James E. Burt, Joseph A. Mason |
| 11. | Physical Geography-Science and Systems of the Human Environment 2009 | Alan H. Strahler, Arthur N. Strallar. |
| 12. | Introduction to Information Technology 2005 | I. T. L. Education Solutions Limited, Itl. |
| 13. | Management Information Systems 2014 | Ken Sousa, Effy Oz |
| 14. | Fundamentals of Telecommunications 2005 | Roger L. Freeman |
| 15. | Basics of Environmental Science 2002 | Michael Allaby |
| 16. | Food Science 1998 | Norman N. Potter, Joseph H. Hotchkiss |
| 17. | Environmental Science: Systems and Solutions. 5th ed. 2013 |
Michael L. McKinney, Robert Schoch and Logan Yonavjak |
| 18. | Environmental Science: A Global Concern 2012 |
William P. Cunningham, Barbara Woodworth Saigo |
| Books for Logical Reasoning | ||
| 19. | Logical Reasoning | Rob P. Nederpelt, Farouz D. Kamareddine |
| 20. | Elements of Logical Reasoning | Jan Von Plato |
| 21. | Reasoning Builder for Admission and Standardized Test |
Staff of Research Education |
| 22. | Test of Reasoning | Thorpe |
| 23. | Mental Ability | Dr. Lal & Jain |
| 24. | The Brain Book: Know Your Own Mind and How to Use it |
Edgar Thorpe |
Current Affairs Syllabus:
Candidates will be expected to display such general knowledge of history, politics and International Affairs, as deemed necessary to interpret current affairs.
I. Pakistan’s Domestic Affairs (20 marks)
- Political
- Economic
- Social
II. Pakistan’s External Affairs (40 marks)
- Pakistan’s relations with its Neighbors (India, China, Afghanistan, Russia)
- Pakistan’s relations with the Muslim World (Iran, Saudi Arabia, Indonesia,
Turkey) - Pakistan’s relations with the United States
- Pakistan’s relations with Regional and International Organizations (UN, SAARC,
ECO, OIC, WTO, GCC)
III. Global Issues (40 marks)
- International Security
- International Political Economy
- Human Rights
- Environment: Global Warming, Kyoto Protocol, Copenhagen Accord
- Population: world population trends, world population policies
- Terrorism and Counter Terrorism
- Global Energy Politics
- Nuclear Proliferation and Nuclear Security
- Nuclear Politics in South Asia
- International Trade (Doha Development Round and Bali Package)
- Cooperation and Competition in Arabian Sea, Indian and Pacific Oceans.
- Millennium Development Goals, Current Status
- Globalization
- Middle East Crisis
- Kashmir Issue
- Palestine Issue
SUGGESTED READINGS
| S.No. | Title | Author |
| 1. | Pakistan Foreign Policy 1947-2005: A Concise History, 2011 | Abdul Sattar, |
| 2. | Issue in Pakistan’s Economy, 2010 | Akbar S. Zaidi |
| 3. | Pakistan: A Hard Country, 2012 | Anatol Lieven |
| 4. | Government & Politics in South Asia, 6th ed., 2009 |
Baxter, Malik, Kennedy & Oberst, |
| 5. | Introduction to International Political Economy, 2010 |
David Balaam & Bradford Dillman |
| 6. | International Organization (Second Edition) 2012 |
Volker Rittberger, Bernhard Zangl and Andress Kruck |
| 7. | The Age of Deception: Nuclear Diplomacy in Treacherous Times (2011) |
Mohamed Elbaradei |
| 8. | International Relations, 2012 | Joshua Goldstein |
| 9. | World Politics: Trends & Transformation, 2011 |
Kegley & Blanton |
| 10. | Pakistan Beyond the Crisis, 2011 | Maleeha Lodhi |
| 11. | Globalization in Question, 2009 | Paul Hirst |
| 12. | International Political Economy: Interests & Institutions in the Global Economy, 2010 | Thomas Oatley |
| 13. | Politics and Change in the Middle East, 10th Ed., Pearson, 2012 |
Andersen, Seibert, and Wagner |
| 14. | Eating Grass: The Making of the Pakistani Bomb, (2012) |
Feroz Khan |
Islamic Studies Syllabus:
I. Introduction of Islam.
- Concept of Islam.
- Importance of Deen in Human Life.
- Difference between Deen and Religion.
- Distinctive Aspects of Islam.
- Islamic Beliefs & its Impact on Individual & Society and the Fundamental of Islam
- Islamic Worships: Spiritual, Moral and Social Impact.
II. Study of Seerah of Prophet Mohammad (PBAH) as Role Model for:
- Individual
- Diplomat
- Educator
- Military Strategist
- Peace Maker
III. Human Rights & Status of Woman in Islam.
- Human Rights and Status of Woman in Islam
- Dignity of Men and Women
IV. Islamic Civilization and Culture:
- Meanings and the Vital Elements
- Role of Civilization in Development of Human Personality and Communities
- Distinctions of Islamic Civilization (Tauheed, Spiritualism, Dignity of Man, Equality, Social Justice, Moral Values, Tolerance, Rule of Law)
V. Islam and World.
- Impact of Islamic Civilization on the West and Vice Versa
- The Role of Islam in the Modern World.
- Muslim World and the Contemporary Challenges.
- Rise of Extremism.
VI. Public Administration and Governance in Islam
- Concept of Public Administration in Islam
- Quranic Guidance on Good Governance
- Concept of Governance and its Applications in the light of Quran, Sunnah and Fiqh.
- Governance Structure in Islam i.e. (Shura, Legislation, Sources of Islamic Law)
- Governance under Pious Khilafat
- Particular letters of Hazrat Umar (R.A) and Hazrat Ali (R.A) to different Authority.
- Responsibilities of Civil Servants System of Accountability in Islam
VII. Islamic Code of Life.
- Salient Features of Islamic Systems, Social System, Political System, Economic System, Judicial System, Administrative System,
- Procedure of Ijmah and Ijtehad.
Islamiat Syllabus in URDU
SUGGESTED READINGS
| Sr. No. | Title | Author |
| 1. | Introduction of Islam | Dr. Hamidullah |
| 2. | Islam: its meaning and Message | Khurshid Ahmad |
| 3. | Islam: The Misunderstood Religion | Muhammad Qutub |
| 4. | Islam at the crass road | MohummadAsad |
| 5. | Islam and the Economic Challenge | Umer Chapra |
| 6. | A brief Survey of Muslim Science and Culture | M. Abdur Rahman |
| 7. | Administrative Development an Islamic Perspective | Muhammad Al-Buraey |
| 8. | Quranic Sciences | Afzalur Rahman |
| 9. | Islamization of Pakistan | Iqbal Zafar |
| 10. | Islamic Law and Constitution | Abul A’ la Mawdudi, |
| 11. | Insan e Kamil | Dr Khalid Alvi |
| 12. | Islami Tehzeeb Kay Chund Darakhshan Pehloo | Mustafa Sabbai |
| 13. | Islam Aur Tahzeeb -e -Maghrib Ki Kash Makash | Dr Muhammad Ameen, |
| 14. | Aurat Maghrib aur Islam | Serwat Jamal Asmaui |
| 15. | Seerat-un-Nabi Vol. I | Shibli Nu’mani |
| 16. | Islam and Secular Mind | Edited by Tarik Jan |
| 17. | Khilafat-o-Malookiat | Abul A’ la Mawdudi, |
RECOMMENDED READINGS:
| 1. | Towards Understanding Islam | Abul A’ la Mawdudi, |
| 2. | Ideals and Realities of Islam | Hussain Nasr, |
| 3. | Administrative Development; an Islamic Perspective, KP.L. London | Alburacy Muhammad A. |
| 4. | Arab Administration | Hussain Shah |
| 5. | The Islamic Republic : Politics, Law and Economy | Hassan Dr. S. Farooq |
| 6. | Studies in Muslim Political Thoughts and Administration | Sherwani, H.K.S. |
| 7. | Reconstruction of Religious Thoughts in Islam | Allama Iqbal |
| 8. | Islamic Political System in the Modern age: Theory and Practice | Ahmad Manzooruddin |
| 9. | Sovereignty-Modern and Islamic: | Ilays Ahmad |
| 10. | Islam in Transition: Muslim Perspectives | Donohue J, John A. and Esposito L. John (eds) |
| 11. | Islam Aik Nazar Main | Sudderud Din Islahi |
| 12. | IslamiNazria e Hayat | Khurshid Ahmad |
| 13. | Islami Nizam e Zindgi aur us kay Bunyadi Tassworat | Abul Aala Maudoodi |
| 14. | Jadah o Manzil | Seyyed Kotub |
| 15. | Islam ka Nizam e Hakoomat | Maulana Hamid ul Ansari |
| 16. | Islami Nizam | Dr Yousof Qerzawi, |
| 17. | Bonyadi Haqooq | Muhammad Salahuddin |
| 18. | Islam Ka Muashi Nizam | Justice Taqi Usamani, |
| 19. | Tahzeeb o Tamaddon e Islami | Rasheed Akhter Nadvi |
| 20. | First Principle of Islamic Economics | Abul A’ la Mawdudi |
| 21. | Islamic Civilization Foundations Belief & Principles | Abul A’ la Mawdudi |
| 22. | Workship in Islam | Abul A’ la Mawdudi |
| 23. | Let us be Muslims | Khurram Murad |
| 24. | Women and Social Justice; an Islamic Paradigm | Prof. Dr. Anis Ahmad |
CSS Optional Subjects Syllabus:
Group-I: (To select one subject of (200 marks) only)
CSS Accountancy and Auditing Syllabus:
Paper-I (MARKS-100)
(A) Financial Accounting (50 Marks)
I. Fundamental Accounting Principles, Concepts, Assumptions and Conventions:
Nature and Scope of Accounting, Accrual/Matching Concept, Consistency of Presentation and Comparability, True and Fair View, Neutrality, Materiality, Prudence, Completeness, Understandability and Usefulness, Going Concern, and Substance over Form.
II. Accounting Cycle/Process and Financial Statements:
Transactions and/or Events, General Journal, General Ledger, Trial Balance (Unadjusted),Adjusting Entries and Adjusted Trial Balance, Work Sheet, Financial Statements including Income Statement, Statement of Financial Position (Balance Sheet), Statement of Cash Flows and Statement of Changes in Equity in accordance with the Financial Reporting Framework as specified by International Accounting Standard Board (IASB) through IFRSs/IASs, and by Securities and Exchange Commission of Pakistan through Companies Ordinance 1984, and Closing and Reversing Entries
III. Attributes, and Significance of Accounting Information:
Attributes of Accounting Information, Information/Reporting Requirements of various Users/Stakeholders of Financial Statements including External (Investors/Shareholders, Creditors, Suppliers, Lenders/Financiers, Government Agencies etc.) and Internal (Board of Directors, Partners, Managers, Employees etc.) Stakeholders.
IV. Accounting for common Legal Forms of a Business:
Accounting Principles and Financial Statements of Sole-proprietorships, Partnerships and Joint Stock Companies including Banking Companies (Excluding Advanced Topics like Amalgamation, Capital Reduction, Consolidation etc.)
V. Accounting for Associations Not-for-profit, and for Public Sector:
Accounting Principles and Financial Statements – of Associations Not-for-profit, and – of Public Sector Entities as per Standardized Financial Reporting Framework provided by International Public Sector Accounting Standards (IPSAS) Board and Practices being followed in the country.
VI. Accounting for Non-current Tangible Assets:
Fundamental Concepts and Principles concerning Non-current Assets: Cost; Depreciable Amount; Depreciation; Fair Value; Property, Plant and Equipment; Residual Value; and Useful Life. Depreciation Methods and their Application (as specified by International Accounting Standards Board):Straight-line Method; Reducing Balance Method; Number of Units Produced and basic know-how of other Methods/Techniques being commonly used by the Industry.
VII. Fundamental and Technical Analysis of various Forms of Organizations:
Financial Statements’ Analysis including both Horizontal (Measuring Change) and Vertical (Ratio) Analysis including Liquidity Ratios, Activity Ratios, Debt Ratios, Profitability Ratios and Market Ratios; Technical and Industry Analysis.
(B) Cost and Managerial Accounting (50 Marks)
VIII. Fundamental Cost Accounting Principles and Concepts:
Nature and Scope of Cost and Managerial Accounting; Cost Concepts, Elements and Classification; Underlying Differences among Financial, Cost, and Management Accounting.
Accounting for Material, Labour and Factory Overheads (FOH):
Recognition and Valuation Principles for Material Inventory, and Methods to control Material Inventory; Calculation/Measurement and Accounting for Payroll for all forms of Labour, Time Rate and Piece Rate Systems; Commonly used Group Incentive Schemes; Factory Overhead Costs and FOH Rate, Departmentalization of FOH Costs, their Allocation, Apportionment and Reapportionment (Primary and Secondary Distributions), Methods for Secondary Distribution including both Repeated Apportionment/Distribution and Algebraic Method.
Costing for Specific Jobs, and Process Costing:
Nature of a Specific Job, and Job-order Costing; Process Flow and Process Costing by the use of Cost of Production Report (CPR).
Management Accounting for Planning, Decision-making and Control: Budgeting and its Use:
Meaning and Nature of a Budget; Major Forms of a Budget including Production and Sales Budget, Cash Budget, Flexible Budgets, Zero-based Budget, Master Budget etc.
Break-even Analysis:
Difference between Marginal and Absorption Costing Techniques; Concept of Relevant Cost; Application and Use of Contribution Margin and other Concepts for Planning and Decision-making (under Break-even Analysis)
Variance Analysis:
Meaning and Use of Standards and Variances; Major Classification of Variances including Material, Labour and FOH Variances, and their Computation.
Paper-II (MARKS-100)
(A) Auditing (40 Marks)
Fundamental Auditing Principles and Concepts:
Audit and Auditing, True and Fair View, Audit Assertions, Reasonable Assurance, Documentation and Audit Evidence, Audit Program, Audit Risks, Computer Information Systems (EDP Systems) and Computer-assisted Audit Techniques (CAAT), Inspection, Fraud, Going Concern, Audit Materiality, Misstatement, Governance and Premise, Tests of Control and Substantive Procedures.
Audit Considerations, Dimensions and Conduct:
Internal Control System and Internal Audit, Internal VS External Audit, Responsibility for Financial Statements, Audit Planning, Scope of an Audit, Objectives of an Audit, Inherent Limitations of an Audit, Risk Assessment and Management, Internal Audit and Corporate Governance, Classification of Audit, Qualities of an Auditor, Auditing in Computer Information Systems (EDP Systems) and Computer-assisted Audit Techniques, General Auditing Principles and Techniques commonly applicable to various Types of Undertakings including Merchandizing, Manufacturing, Banking, Insurance, Investment Entities etc., Audit Performance and Audit Completion.
Role and Responsibilities of an Auditor:
Auditor’s professional and legal Rights, Responsibilities & Duties, and Liabilities; Auditor’s Opinion and Report, and their classification (Types); – as specified under the Companies Ordinance 1984, and in the handbook of IFAC.
(B) Business Taxation (30 Marks)
1.Tax Structure, and Fundamental Concepts vis-à-vis Income Tax in Pakistan:
Tax Structure in Pakistan; Fundamental Definitions/Terminologies defined under Section 2 of the Income Tax Ordinance 2001.
2.Income Tax and Sales Tax Principles, and their Application:
Selected Provisions from Income Tax – Income for Tax Purposes [Section 4, 9 & 10], Heads of Income [Section 11], Tax Payable on Taxable Income [First Schedule to the Ordinance], Salary Income and Taxation [Sections 12 to 14], Income from Property [Sections 15 & 16], Income from Business[Sections 18 to 20], Capital Gains[Sections 37 to38], Income from other sources[Section 39, 40, 101(6), 111],Tax Credits [Sections 61 to 65], Taxation of Individuals, AOPs and Companies [Sections 86, 92, 94], Due Date for Payment of Tax [Section 137], Deduction of Tax at Source/With-holding Tax [Sections 147, 149, 153, 155]and related Income Tax Rules 2002. Selected Definitions and Provisions from Sales Tax –Scope of Tax [Section 3], Exempt supply [Section 2(11)], Goods [Section 2(12)], Input Tax [2(14)], Registered person [Section 2(25)], Supply [Section 2(33)], Tax [Section 2(34)], Retail Price and Retailer [Section 2(27)& 2(28)], Taxable Activity [Section 2(35)], Taxable Supply [Section 2(41)], Tax Fraction [Section 2(36)], Tax Period [Section 2(43)], Time of Supply [Section 2(44)], and Determination of Tax Liability [Section 7].
(C) Business Studies, and Finance (30 Marks)
Business Studies:
Nature and Scope of a Business Entity, Contemporary Challenges posed to a Business; Common Legal Forms of a Business Entity – Sole proprietorship, Partnership, Joint Stock Company, their Features, Formation and Management; Business Combinations and their Scope; Business Cycle and its Implications; Role of Information Technology in Business.
Finance:
Meaning, Nature and Scope of Finance, and Financial Management; Common Modes (Types) of Business Finance – Short-, Medium-, and Long-term Financing; Nature and Scope of Financial Markets and Institutions; Features and Classification of Financial Markets; Financial Management Techniques for Decision making: Time Value of Money, Cost of Capital and Capital Budgeting Techniques.
Suggested/Recommended Readings:


Economics Syllabus CSS:
Paper-I (100 Marks)
I. Micro Economics:
Consumer behaviour, Determination of market demand and supply i.e. concept of elasticity of Demand & Supply, Static, Comparative Static Analysis, Distinction between partial and general equilibrium analysis (basic level), theory of the Firm, Producer’s equilibrium, Pricing of the factors of production.
II. Macro Economics
Basic Economic Concepts, National Income Accounting, Consumption Function, Multiplier, Accelerator, Component of Aggregate Demand, Labour Demand and Supply, Un-Employment, Determination of equilibrium level of income and output (at least with reference to two or three “schools of thought”), Inflation.
III. Money and Banking
Functions of Money, Quantity Theory of Money, The Fisher and Cambridge Formulations, Systems of note issue, Credit Creation, Functions of Central Banks, Instruments of Credit Control, Distinction between Goals, Operational & Intermediate Target of Central Banks Policy, Concept of Reserves, Liquidity Premium, Term Structure of Interest Rate, etc; Transmission Mechanisms of Monetary Policy, Theory of Liquidity Preference. TVM, Capital Structure, Capital Restructuring, IS-LM Analysis and The role of Central Bank, Money Demand and Supply.
IV. Public Financing
Government expenditure, Sources of Government Revenue, Privatization, Taxes and nontaxes, Incidence of different taxes, Public Debt, Objectives, methods of repayment, Deficit financing, General Equilibrium Analysis, Welfare Economics, Fiscal Policy.
V. International Trade
Theories of comparative advantage and Factor Endowments, Trade & Growth, Colonialism, Imperialism and International Trade, Trade Restrictions, Economic Integration, Trade Policy, Balance of Payments, Foreign Exchange, International Monetary system, Custom Unions.
VI. Economic Development
Concepts of development, Human development, Historical growth process and Development, Theories of development, structural issues of development, Income distribution and poverty, sectoral (agricultural, Industry, trade and fiancé) issues and development, environment and development.
Paper-II (100 Marks)
(Economics of Pakistan)
I. Definition and Measurement of Development:
Characteristics of under development, rethinking on the concept of development: Growth vs. Redistributive justice, Absolute and Relative Poverty, Basic Needs Approach, Sustainable Development, Environmental Degradation & other Issues.
II. Planning Experience of Pakistan:
A critical evaluation of the strategy of economic planning, governance & Institutions.
III. Agricultural Development in Pakistan:
Changes in Agricultural Policies over plan periods, Major Monetary and Fiscal measures to promote Agricultural development, Green Revolution Strategy and its implications for growth and redistribution, Land Reforms and changes in the Tenure System 1950—1980, Cooperative Farming, Rural Development.
IV. Industrial Development in Pakistan:
Early industrialization strategy, Creation of Financial and Development Institutions, Major monetary and fiscal measures to promote industrial development, changing role of public sector over the plan periods, Evaluation of Nationalization Policy, Concentration of industrial income and wealth, Evaluation of Import Substitution Policy and Export led Growth Strategy in Pakistan.
V. Role of Foreign Trade and Aid in Economic Development :
Trends in Pakistan’s Balance of Payments, Terms of Trade, Changes in direction of trade, Trends in Pakistan’s major exports and imports, Causes of significant changes in the trends, the role of migration and remittances in Pakistan’s economy, costs and benefits of Foreign Aid, Role of Foreign Investment.
VI. Privatization, Denationalization, Deregulation:
conceptual and operational aspects. International comparisons. Pakistan Experience of Privatization.
VII. Interest Free Banking in Pakistan
VIII. Energy Policy of Pakistan
IX. Social Sector Development in Pakistan
X. Major Issues in Pakistan Economy:
Energy crisis, Corruption, Bad governance, External debt accumulation and dependency, Unemployment, Income inequality, Inflation,
Fiscal and trade deficits, Balance of payment issues, Shortage of irrigation water.
SUGGESTED READINGS
1. A Text-book of Economics Theory by Stonier & Hague
2. Economic Development by Todaro, M.P.
3. Under Development and Agrarian Structure in Pakistan by Khan, Mahmood Hassan
4. Economic of Islam by Ahmed, S.M.
5. Economics by Paul A. Samuleson
6. Factors in Economic Development by Cairncross, A.K
7. Foreign Aid Theory and Practice in Southern Asia by Wolf, Jr. DC
8. Government Finance—An Economic Analysis by Due John, F.
9. Introduction to International Economics by Snider, D.A, Paul Krugman, Donimich Salvatore
10. Microeconomic by Ferguson, C.E. & Gould, J.P., Nicholson, Mankiw
11. Macroeconomics by Rudigar Dorubush and Stanley Fisher Blanchard
12. Population Problems Theompson & Lewis
13. Studies in Economic Development with Special Reference to Pakistan by Ghouse, A.
14. History of International Trade Findlay, R and O’ Rourke, K
15. Colonialism and Modernization Karl Marx Anchor books
16. On Colonialism Karl Marx and Frederick Engels,
17. Economic Survey of Pakistan Government Publication

Computer Science Syllabus:
Paper-I (100 Marks)
Section-A (50 Marks)
I. Introduction to Computing, Introduction to Information Technology and Computers, History of Computing, Computer HW and SW Details, Computer System Components and Communication System, Input & Output devices and their types, Storage Media and their types, Types of Computer Hardware, Software, and Programming languages, Information Representation & Number Systems, User interfaces, Major Software Issues, Creation, formatting, and maintenance of
Computer documents, Usage of Word processors, Spread sheets, Power-Point, Email, Search Engines, Browsers, Messengers, and Internet , Computers & Society, Information Security/Privacy, Computer Crimes and Ethical Challenges, Viruses, Plagiarism, Intellectual Property Rights, Difference between computer science, software engineering, information technology, information systems, computer engineering and bioinformatics; IEEE / ACM computing disciplines guidelines.
II. Programming Fundamentals
Basic programming elements and concepts, Problem Solving & Program Design, Components of a programming language, Program development and execution, Program structure, Data types and variable declarations, Standard I/O streams, and statements, Control structures, Standard library functions, User defined functions and parameter passing, Arrays, pointers, and strings, Structures, unions, and bit manipulation operators.
III. Object Oriented Paradigm
Object Oriented Programming Concepts ( Object-oriented paradigm, data abstraction, encapsulation, inheritance, Polymorphism), Introduction to Classes and Objects ( classes, objects, data members, member functions), Classes Advanced ( friends, static, composition, this, const), Operator overloading (stream insertion, stream extraction, binary operator, unary operator), Inheritance (single inheritance, multiple inheritances, protected members, method over-riding), Polymorphism (virtual function, pure-virtual functions, abstract class, abstract super class), Standard Template Library (STL), Files & streams (sequential access files, random access files), File processing, Exception Handling
Section-B (50 Marks)
IV. Algorithms & Data Structures
Fundamental concepts, Properties of algorithms, Criteria for an Algorithm, Parameters for selecting an algorithm, Algorithm Representations, Pseudo Code and Flow Charts, Designing Algorithms, Algorithm Analysis and Asymptotic Notations, Classification of Lists, Abstract Data Types, Implementation of Stacks and Queues using ADTs, Searching and Sorting Algorithms (Linear Search, Binary Search, Bubble Sort, Merge Sort, Quick Sort, Heap Sort), Stacks and Queues, Hash Tables (Linear Probing, Bucketing, Chaining), Recursion, Trees (Binary Trees, Binary Search trees, AVL Trees, Two-Three Trees), Graphs, Heuristic (Guided) Search, Genetic Algorithms, Encryption Algorithms (DES, RSA)
V. Software Engineering
Software Processes, Software Process Models, Agile Software Development, Analysis Modelling, Requirements Engineering, Design Concepts, Architectural Design, Design & Implementation, Software Testing, System Delivery and Maintenance, Software Evolution Formal Specification, Software Quality Assurance, Introduction to Proofs of Correctness (LNO), Distributed Software Engineering, Aspect-Oriented Software Engineering, Project Management, Process Improvement
VI. Compiler Construction
Difference among various type of Translators, Phases of Compilers, Classification of Compilers, Lexical Analysis (Input buffering, Specification & Recognition of tokens, Regular expressions, Finite automata, Syntax Analysis (Context-free grammars and their classification, LL(k) vs. LR(k) grammars, Top-down vs. Bottom-Up parsers, Parsing Techniques, FIRST and FOLLOW sets, Predictive Parsing using LL(1) grammars, Syntax error handling and recovery strategies), Syntax Directed Translation (Synthesized attributes, Inherited attributes, Construction of syntax trees, Top-down translation), Semantic analysis (Symbol tables, Type Expressions, Type Checking of statements), Intermediate Code Generation, Code Generation (Issues in the design of code generation, The target machine, Run-time storage management, Register allocation), Code optimization (Elimination of Redundant code, Folding of Constant, Loop optimization, Peephole optimization, Problems of optimization)
Paper-II (100 Marks)
Section-A (50 Marks)
I. Computer Organization & Architecture
Fundamental concepts, Overview of a Computer System, Evolution & Performance Languages, Architectural levels, Virtual machines, Processor types, Metrics, Machine instructions, Instruction execution cycle, CISC vs. RISC, Parallelism, Internal/External data representation, Computer Function and Interconnections, Cache Memory, Internal Memory, External Memory, Input /Output System, Computer Arithmetic Microprocessor and its Bus Structure, I/O Types, Types of Buses, Memory Organization and Structure, information flow and execution in Machine, Instruction Representation, Machine Instruction Characteristics, Instruction Processing, Processor Structure & Function, Control Unit Operation, Micro-programmed Control, Instruction-Level Parallelism And Superscalar Processors, Parallel Processing, Multi-Processor and Multi-core Systems
II. Computer Communications & Networks
Basic Concepts and Classification of Networks, Circuit switching, Packet switching, Multiplexing (TDM, FDM), Layering: OSI and TCP/IP, Application Layer (Network application architectures, HTTP, FTP, Email, DNS, P2P applications), Transport Layer
(Multiplexing in UDP and TCP, Connectionless Transport: UDP, Reliable data transfer and TCP, Congestion avoidance and control), Network Layer (The Internet Protocol, IPv4 Datagram, Internet Address Classes, Special IP Addresses ARP, IPv6, ICMP, Network Address Translation (NAT), Internet Routing Protocols and Algorithms, X.25, Frame relay and ATM, MPLS), Physical & Link Layer Functionalities (Error Detection & Control, ARQ, Link layer addressing, LAN Technologies, Bridges and Hubs, Multiple Access), Special topics (Security, Overlay networks, naming, Content distribution networks, Peer to peer systems, DHTs, Network Attacks)
III. Operating Systems Concepts
Roles of an Operating System, Operating-System Evolution, Structures, and Operations, Classification of Operating Systems, Computing Environments, Design and Components of OS, Process Management, Process Synchronization, Deadlocks, Memory Management, Virtual Memory Management, File Systems (UNIX and Windows Systems), I/O Management
Section-B (50 Marks)
IV. Database Systems
Introduction to Database Systems, Relational Data Model & Relational Database Constraints, Relational Data Model, SQL, Relational Algebra & Calculus, ER Model, ER to Relational Mapping, PL/SQL Stored Procedures & Triggers, Functional Dependencies and Normalization, Storage & Indexing, Indexing Structure, XML documents & Web Services, Query Processing & Evaluation, Query Optimization, Transaction processing, Object-Oriented Databases, Distributed Databases, Database Security & Access Control
V. Digital Image Processing
The relation between Image Processing, Computer Graphics, Computer Vision and Artificial Intelligence; Image Sensing and Acquisition Techniques; Representing Digital Image; Image Sampling and Quantization; Image Storage and Operations; Image Transformations (Translation, Scaling, Rotation, Shear); Image Histogram; Image Enhancement (Contrast, Smoothing, Sharpening); Gray-scale and Color Images; Color Models (RGB, CMYK and HIS); Image Restoration; Noise Models; Morphological Operators (Erosion, Dilation, Opening, Closing, Skeletonization, Thinning); Image Segmentation; Point Detection, Line Detection, Edge Detection and Boundary Detection; Image Compression
VI. Web Engineering & Technologies
Modelling techniques for web applications, Introduction to web engineering, requirement engineering, requirement, types of requirements, functional requirements, non functional requirements, Requirement engineering process (Elicitation and negotiation, Documentation, Validation and verification, Management), HTML(hypertext markup language), Software Architecture, Styles, Patterns, and frameworks, Components of Web Architecture, Classifications of web architecture , Web Application layered architecture (client server, n- layered, JSP model, struts, OOHDM ), Integration Architecture, Data Aspect architectures, Cascading Style Sheet(CSS), CSS properties, JavaScript (Functionalities, Events, Variables, Operators), DOM(Document Object Model), XML, RSS, API, Client-side programming using (HTML, XHTML, XML, JavaScript, and CSS), Server side programming using PHP, Web development process, Web Application Development Methodologies, Web site promotion and deployment, Web applications Issues (Accessibility, testing, performance, operation, maintenance, security)
Suggested Readings
Political Science Syllabus:
PAPER I- (Marks – 100)
Part-A (50 Marks)
I. Western Political Thought:
Plato, Aristotle, Machiavelli, Montesquieu, Hobbes, Locke, Rousseau, Kant, Mill, Bentham, Hegel, Marx, Lenin, Mao, Gramsci, Karl Popper, Pierre Bourdieu, John Rawls, Frances Fukuyama, Foucault, Derrida, Kierkegaard, Jean Paul Sartre, Rene Descartes.
II. Muslim Political Thought:
Al-Farabi, Al-Mawardi, Ibn Rushd, Imam Ghazali, Ibn Taymiyyah, Nizam-ul-MulkTusi, Ibn Khaldun, Shah Waliullah, Allama Muhammad Iqbal, Jamaluddin Afghni, Rashid Rida.
Part -B (50 Marks)
III. State System:
The nature and emergence of modern nation-state system, Islamic concept of state and Ummah.
IV. Political Concept (Western and Islamic):
Sovereignty, Justice, Law, Liberty, Freedom, Equality, Rights and Duties, Human Rights, Political Authority and Power.
V. Comparative Politics:
Political Socialization, Political Culture, Political Development, Political Recruitment, Social Change, Civil Society, Violence and Terrorism in Politics, Gender and Politics, Women Empowerment.
VI. Political Participation:
Political Change and Revolution, Elections, Electoral System, Public Opinion, Propaganda, Political Parties, Pressure Groups and Lobbies.
VII. Political Institutions and Role of Government:
Legislature, Executive, Judiciary, Political Elites, Civil and Military Bureaucracy.
VIII. Forms of Government:
Monarchy, Democratic, Dictatorship, Totalitarian/Authoritarian, Unitary, Federal, Confederation, Presidential and Parliamentary.
IX. Political Ideologies:
Capitalism, Marxism, Communism, Socialism, Totalitarianism, Fascisms, Nationalism, Islamic Political Ideology.
X. Local Self Government:
Theory and practice of Local Self-Government with special reference to Pakistan, Comparative analyses of systems of local governance, Public Administration and Public Policy.
PAPER-II (MARKS-100)
Part-A (30 Marks)
I. Comparative and Analytical Study of the Political Systems:
Political System of U.S.A, U.K, France and Germany
II. Global and Regional Integration
Globalization and Politics, Global Civil Society, Regional politico economic integration and organizational structure of the European Union, SAARC, ECO, International Financial Regimes IMF and WTO.
Part-B (70 Marks)
III. Comparative and Analytical Study of the Political Systems:
Political system of Turkey, Iran, Malaysia, India and China.
IV. Political Movements in India (Colonial Period):
Rise of Muslim Nationalism in South Asia and Pakistan Movement (with special reference to the role of Sir Syed Ahmed Khan, Allama Muhammad Iqbal and Quaid-i-Azam Mohammad Ali Jinnah)
V. Government and Politics in Pakistan:
Constitution making from 1947 -1956, A comparative and critical analysis of 1956, 1962, 1973 Constitutions of Pakistan, Constitutional Amendments up-to-date, Federal Structure in Pakistan, and Central-Provincial relations after 18th amendment, Political Culture of Pakistan, Political Developments and the Role of Civil and Military Bureaucracy, Judiciary, Feudalism, Dynastic Politics, Political Parties and Interest Groups, Elections and Voting Behavior, Religion and Politics, Ethnicity and National Integration.
VI. International Relations:
History of International Relations: Post World War-II (WW-II) Period.
Foreign Policy of Pakistan: National Interests and Major Determinants i-e
1). Size/Geography
2). Economic Development
3). Security
4). Advancement in Technology
5). National Capacity
6). Political Parties/Leadership
7). Ideology
8). National Interest
9). Role of Press/Bureaucracy
10). Social Structure
11). Public Opinion
12). Diplomacy.
13). Foreign Policy-making Process in Pakistan
Also External Factors like International Power Structure, International Organizations, World
Public Opinion and Reaction of other States.
Recommended Books for CSS Political Science:
PAPER: INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS (200 MARKS)
![]()
Paper—1 (Marks-100)
I. Introduction
- The Definition and Scope of International Relations.
- The Nation-State System
- Evolution of International Society
II. Theories and Approaches
- The Classical Approaches-Realism and Idealism
- The Scientific Revolution-Behavioral Approach, System Approach,
- Neo-realism, Neo-liberalism.
- Post-modernism, Critical Theory, Feminism, Constructivism
III. International Political Security.
- Conceptualization of security in the Twenty-First century
- Power. Elements of National Power
- Balance of Power
- Foreign Policy: Determinants, Decision Making and Analysis
- Sovereignty
- National Interest
IV. Strategic Approach to International Relation.
- War: Causation of War, Total War, Limited War, Asymmetric Warfare, Civil War, Guerilla Warfare
- Strategic Culture: Determinants of Pakistani Strategic Culture.
- Deterrence: Theory and practice with special reference to India and Pakistan
V. International Political Economy.
- Theories in IPE: Mercantilism, Economic Liberalism, and Neo- Marxism
- Theories of Imperialism, Dependence and Interdependence discourse
VI. International political community.
- Nationalism
- Internationalism
- Globalization
VII. Approaches to Peace
- Diplomacy
- International Law
- Arms Control /Disarmament and Nuclear Non proliferation Regime
VIII. International Political Institution
- United Nations
- International Monetary Fund (IMF)
- World Bank
- International Court of Justice
Paper- II (Marks-100)
I. International Relation between two Wars
- Russian Revolution, Fascism, League of Nations, Second World War
II. Cold War
- Decolonization in Asia and Africa.
- Rise of United States and Soviet Union,
- Era of Tight Bipolarity, Détente and Loose Bipolarity, Revival of Cold War
III. Post Cold War
- End of History, Clash of Civilizations, Terrorism, Globalization, Unipolarity (New World Order) and Revival of Multi-Polarity
IV. International and Regional Organizations
- League of Nations, United Nations, Regional Organizations, EU, ASEAN, NAFTA, SAARC, SCO, OIC, ECO, WTO.
- Reforms in the United Nations, World Bank and the IMF
V. Foreign Policy of Selected Countries
- USA, Russia, China, UK, India, Pakistan and EU
VI. South Asia
- Peace-making and Peace-Building in South Asia: Analytical overview of peace processes between/among the states of South Asia especially between India and Pakistan.
- India and Pakistan: Overview of agreements and accords, Indus Water Treaty; Composite Dialogue; Sir Creek & Siachen border, Visa and People to people contact; Trade; and Role of civil society
- Afghanistan: Cold war theatre; Soviet Invasion and Mujahedeen; Geneva Accord; Post Cold War situation—Rise of Taliban, AL-Qaeda & 9/11; Operation Enduring Freedom; The Bonn Process- Withdrawal
VII. Weapons of Mass Destruction
- Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons
- Nuclear Weapon States- Programs and Postures: Indian Pakistan Nuclear Doctrines
- Nuclear Non –Proliferation Regime: International Atomic Energy Agency, Nuclear Non- Proliferation Treaty; Nuclear Supplier Group; Partial Test Ban Treaty; Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty; Fissile Material Cut-off Treaty
- Challenges of Non-Proliferation, Cooperation for Nuclear Energy
- The Missile Defence Systems and their impact on global strategic environment
- Militarization and Weaponization of Space.
VIII. Contemporary Issues
- Euro-Atlantic Vs. Asia Pacific: Great Power Policies
- Kashmir Issue
- Palestine Issue
Suggested Readings
Group-II: (To select subject(s) of 200 marks only)
PHYSICS Syllabus (200 MARKS)
PAPER—I (Marks-100)
I. Mechanics
◼ Vectors: Dots, Cross and triple products, Gradient, divergence, curl and applications.
◼ Newtonian laws of motion: calculus based approach to kinematics, forces and dynamics, conservation law of energy; conservation of linear and angular momentum; Dynamics of rigid body; spin and precession; gyroscope; Gravitation; planetary motion and satellites; Kepler’s laws; centripetal forces
◼ Special theory of relativity: Michelson-Morley experiment and Einstein’s postulates; Lorentz transformation; time dilation and length contraction; equivalence of mass and energy.
II. Fluid Mechanics
◼ Surface tension; Viscosity; Elasticity; fluid motion and Bernoulli’s theorem.
III. Waves and Oscillations, Optics
◼ Free oscillation with one and two degrees of freedom; forced and damped oscillations and phenomenon of resonance; Simple harmonic motion; Traveling waves and transmission of energy; Phase and Group velocity; standing waves; Basics of sound waves.
◼ Reflection, Refraction, Interference, Diffraction and Polarization of waves; interferometer and Newton’s rings; Diffraction Gratings and their resolving power; spectrometers. Electromagnetic wave equation; normal and anomalous dispersion; coherence, lasers and applications.
IV. Heat and Thermodynamics
◼ Perfect gas, real gas and Van der Waals equation; Three Laws of Thermodynamics; internal energy; temperature; entropy; Thermal properties of simple systems; kinetic theory of gases; Maxwellian distribution of molecular velocities; Brownian motion; Transport phenomena. Classical Maxwell-Boltzmann Statistics and its application; Bose-Einstein and Fermi-Dirac Statistics.
PAPER—II (Marks-100)
I. Electricity and Magnetism
◼ Electric field due to point charges; Gauss’ law; Electric potential; Poisson and Laplace’s equations; Dielectric medium and Polarization; Capacitance; Moving charges and resulting magnetic field; Ampere’s law; Magnetic properties of matter; Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction; Alternating current and RLC circuit; Poynting theorem and Poynting Vector. Maxwell’s equations in integral and differential form; scalar and vector potential.
II. Modern and Quantum Physics
◼ Waves and particles and De Broglie’s Hypothesis; Operators and quantum states; observables; time dependent and independent Schrodinger equation; angular momentum; spin 1/2 particle in a magnetic field; wave mechanics; particle in a box; tunnelling; one-dimensional harmonic oscillator; Heisenber’s uncertainty relationship and indeterminacy based on commutation properties of operators; Bohr’s theory and quantum numbers including electron spin; Pauli’s exclusion principle; Spectra of simple systems with one or two valence electrons; photo electric effect; Compton scattering; pair production; Lande’s g factor and Zeeman effect. Raman effect;
III. Solid State Physics
◼ Crystal lattice and structure, Bravais lattice, free electron model, Band theory and electron in a periodic potential, Fermi energy and density of states, n and p type semiconductors, physics of the transistor and MOSFET, dielectric properties, magnetic properties and origin of magnetism.
IV. Nuclear Physics
◼ Structure of Nuclei; Radioactivity,, and decay; Methods of detection of nuclear radiation, Mass Spectrometer; Accelerators; Phenomenon of fission; reactor and nuclear power; nuclear fusion and its applications; Elementary particles and their properties.
SuggestedBooks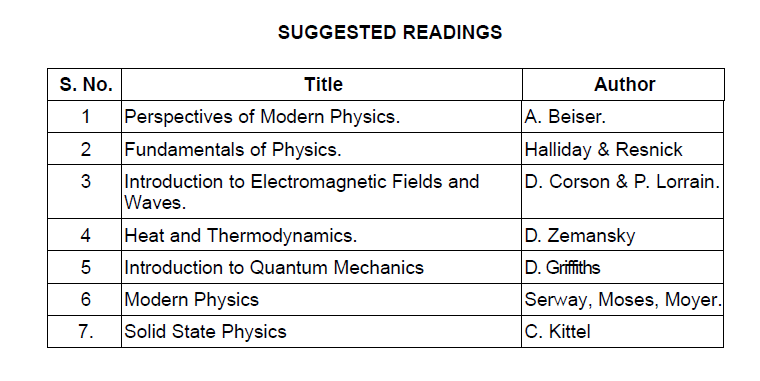
Download Physics Past Papers Download Physics Books Download Full CSS Syllabus
CSS Chemistry Syllabus:
Paper-I (100 Marks)
I. Atomic Structure and Quantum Chemistry
Electromagnetic spectrum, photoelectric effect, Bohr’s atomic model, wave and particle nature of light matter, de Broglie’s equation, Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle, wave functions and Born interpretation of wave functions, probability density, Eigen functions and Eigen values, Hamiltonian operator, Schrödinger wave equation and its solution for particle in one and three dimensional box.
II. Electrochemistry
Ions in solution, measurement of conductance and Kohlrausch’s law, mobility of ions and transport number, conductometric titrations, Debye-Hückel theory and activity coefficient, determination of activities, Redox reactions, spontaneous reactions, electrochemical cells, standard electrode potentials, liquid junction potential, electrochemical series, Nernst’s equation, measurement of pH, electrolytic cells, potentiometry, reference and indicator electrodes, fuel cells, corrosion and its prevention.
III. Thermodynamics
Equation of states, ideal and real gases, the Van der Waals equation for real gases, critical phenomena and critical constants, four laws of thermodynamics and their applications, thermochemistry, calorimetry, heat capacities and their dependence on temperature, pressure and volume, reversible and non-reversible processes, spontaneous and non-spontaneous processes, Hess’s law, The Born-Haber cycle, relations of entropy and Gibbs free energy with equilibrium constant, Gibbs Helmholtz equation, fugacity and activity.
IV. Chemical Kinetics
The rate and molecularity of reactions, Factors affecting rate of a chemical reaction, zero, first, second and third order reactions with same initial concentrations, half lives of reactions, experimental techniques for determination of order of reaction (integration, half-life, initial rate and graphical methods), collision theory, transition state theory, Arrhenius equation and rate equations of complex reactions.
V. Surface Chemistry and Catalysis
Properties of liquids, physical and chemical properties of surface, determination of surface area. Adsorption and absorption; physical adsorption and chemisorption, adsorption isotherms, Langmuir adsorption isotherm and Freundlich Adsorption isotherm. Colloids; properties, classification and preparation of colloidal systems. Surfactants, Phase rule; Gibbs equation of phase rule, one component systems, two component systems and their examples, Catalysis; homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis, acid-base and enzyme catalysis.
VI. Fundamentals of Chemo-metrics
Sampling, significant figures, stoichiometric calculations, measurement errors, analysis of variance (ANOVA), arithmetic mean, median, mode, standard deviation/relative standard deviation, confidence limits, Gaussian distribution, least square method, Statistical tests.
VII. Separation Methods
Solvent extraction; theory of solvent extraction; solvent extraction of metals, analytical separations, multiple batch extraction and counter current distribution. Chromatography; theory of chromatography, classification and overview of chromatographic techniques (paper, thin layer, column and ion exchange chromatographies). Principle of electrophoresis and its application as separation and characterization of proteins.
VIII. Basic Inorganic Chemistry
Types of chemical bonding, ionic and covalent bonding, localized bond approach, theories of chemical bonding, valance bond theory (VBT), hybridization and resonance, prediction of molecular shapes using valence-shell electron-pair repulsion (VSEPR) model, Molecular orbital theory (MOT) applied to diatomic molecules, delocalized approach to bonding, bonding in electron deficient compounds, hydrogen bonding, Physical and chemical properties of p-block elements with emphasis on oxygen, carbon, chlorine, silicon, nitrogen, phosphorus and some of their representative compounds.
IX. Acids and Bases
Brief concepts of chemical equilibrium, acid–base theories including soft and hard acid and base (SHAB) concept, relative strength of acids and bases, significance of pH, pKa, pKb and buffer solutions. Theory of indicators, solubility, solubility product, common ion effect and their industrial applications.
X. Chemistry of d and f-block elements
General characteristics of d-block elements, historical back ground of coordination chemistry, nomenclature and structure of coordination complexes with coordination number 2-10, Chelates and chelate effect. Theories of coordination complexes; Werner’s theory, Valence bond theory (VBT), Crystal field theory (CFT) and Molecular orbital theory (MOT). Jahn-Teller theorem, magnetic properties, spectral properties, isomerism, stereochemistry and stability constants of coordination complexes.
General characteristics of Lanthanides, occurrence, extraction and general principles of separation, electronic structure and position in the periodic table, lanthanide contraction, oxidation states, spectral and magnetic properties and uses. General characteristics of actinides, electronic structure, oxidation state and position in the periodic table, half-life and decay law.
Paper-II (100 Marks)
I. Basic Concepts of Organic Chemistry
Bonding and orbital hybridization, Localized and delocalized bonding, Inductive effect, Dipole moment, Resonance, Hyperconjugation.
II. Saturated and Unsaturated Hydrocarbon
Nomenclature, Physical properties, Preparation and reactions of alkanes, alkenes and alkynes.
III. Chemistry of Aromatic Compounds
Benzene structure, Aromaticity, Mechanism of electrophilic substitution reaction, Activating and deactivating substituents, Effect of substituents on orientation and reactivity.
IV. Chemistry of Functional Groups
Preparation and properties of alcohols, phenols, ethers, and amines with focus on reaction mechanism and applications. Preparation and reactions of alkyl halides. Synthetic applications of Grignard reagent. Carbonyl compounds, preparations and reaction mechanism of aldehydes and ketones and their applications. Carboxylic acids and their derivatives, acidity of carboxylic acids and effect of substituents on their acidity, preparation and reactions of carboxylic acids and their derivatives including acid halides, acid anhydrides, esters and amides.
V. Aliphatic nucleophilic substitution and elimination reactions
Mechanism of nucleophilic substitution reactions. Elimination reactions, Zaitsev rule and Hofmann rule. Competition between Substitution and elimination reactions.
VI. Stereochemistry
Molecular chirality. Types of stereoisomers. R,S configuration and E,Z designation. Optical activity, Stereoselectivity and stereospecificity. Resolution of racemic mixtures.
VII. Organic Spectroscopy
Theory, Principle, instrumentation and applications of UV/Visible, 1H NMR, IR spectroscopy and Mass spectroscopic techniques.
VIII. Biomolecules
Carbohydrates; Monosaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides, biological functions of starch, glycogen, cellulose, and cell wall polysaccharides. Lipids; Classification and biological importance of lipids. Significance of lipids in biological membranes and transport mechanism.
Amino Acids; Classification of amino acids. Physical and chemical properties of amino acids. Biological significance. Proteins; Classification. Properties and biological significance. Primary, secondary tertiary and quaternary structures.
Nucleic Acids; Chemical composition of nucleic acids. Structure and biological significance of nucleic acids. Enzymes; Enzyme-substrate interactions and nature of active site, mechanism of enzyme action, kinetics of single substrate reactions, enzyme inhibition, regulatory enzymes and allosteric enzymes.
IX. Metabolism
Digestion; absorption and transport of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and nucleic acids. Glycolysis; citric acid cycle, gluconeogenesis, glycogenesis, glycogenolysis and photosynthesis.
Biosynthesis of triglycerides, phosphides, steroids and bile acids and ketone bodies.
Biochemical reaction of amino acids: decarboxylation, deamination, transamination and transmethylation, etc., urea cycle, creatine and uric acid synthesis.
Catabolism of nucleosides, DNA polymerases and other enzymes involves in metabolism.
X. Chemical Industries
Manufacturing and processing of sugar, cement, glass, paper, fertilizers, soap and detergents.
SUGGESTED READINGS
Download Chemistry Past Papers Download Chemistry Books
CSS APPLIED MATHEMATICS Syllabus: (100 MARKS)
I. Vector Calculus (10%)
Vector algebra; scalar and vector products of vectors; gradient divergence and curl of a vector; line, surface and volume integrals; Green’s, Stokes’ and Gauss theorems.
II. Statics (10%)
Composition and resolution of forces; parallel forces and couples; equilibrium of a system of coplanar forces; centre of mass of a system of particles and rigid bodies; equilibrium of forces in three dimensions.
III. Dynamics (10%)
Motion in a straight line with constant and variable acceleration; simple harmonic motion; conservative forces and principles of energy.
Tangential, normal, radial and transverse components of velocity and acceleration; motion under central forces; planetary orbits; Kepler laws;
IV. Ordinary differential equations (20%)
Equations of first order; separable equations, exact equations; first order linear equations; orthogonal trajectories; nonlinear equations reducible to linear equations, Bernoulli and Riccati equations.
Equations with constant coefficients; homogeneous and inhomogeneous equations; Cauchy-Euler equations; variation of parameters.
Ordinary and singular points of a differential equation; solution in series; Bessel and Legendre equations; properties of the Bessel functions and Legendre polynomials.
V. Fourier series and partial differential equations (20%)
Trigonometric Fourier series; sine and cosine series; Bessel inequality; summation of infinite series; convergence of the Fourier series.
Partial differential equations of first order; classification of partial differential equations of second order; boundary value problems; solution by the method of separation of variables; problems associated with Laplace equation, wave equation and the heat equation in Cartesian coordinates.
VI. Numerical Methods (30%)
Solution of nonlinear equations by bisection, secant and Newton-Raphson methods; the fixed- point iterative method; order of convergence of a method.
Solution of a system of linear equations; diagonally dominant systems; the Jacobi and Gauss-Seidel methods.
Numerical differentiation and integration; trapezoidal rule, Simpson’s rules, Gaussian integration formulas.
Numerical solution of an ordinary differential equation; Euler and modified Euler methods; Runge- Kutta methods.
SUGGESTED READINGS
CSS APPLIED MATHEMATICS Past Papers CSS APPLIED MATHEMATICS Books
Pure Mathematics CSS Syllabus:
Section-A (40- marks)
I. Modern Algebra
» Group, subgroups, Lagranges theorem, Cyclic groups, Normal subgroups, Quotient groups. Fundamental theorem of homomorphism. Isomorphism theorems of groups, Inner automorphisms. Conjugate elements, conjugate subgroups. Commutator subgroups.
» Ring, Subrings, Integral domains, Quotient fields, Isomorphism theorems, Field extension and finite fields.
» Vector spaces, Linear independence, Bases, Dimension of a finitely generated space. Linear transformations, Matrices and their algebra. Reduction of matrices to their echelon form. Rank and nullity of a linear transformation.
» Solution of a system of homogeneous and non-homogeneous linear equations. Properties of determinants.
Section-B (40- marks)
II. Calculus & Analytic Geometry
» Real Numbers. Limits. Continuity. Differentiability. Indefinite integration. Mean value theorems. Taylor’s theorem, Indeterminate forms. Asymptotes. Curve tracing. Definite integrals. Functions of several variables. Partial derivatives. Maxima and minima. Jacobnians, Double and triple integration (techniques only).Applications of Beta and Gamma functions. Areas and Volumes. Riemann-Stieltje’s integral. Improper integrals and their conditions of existences. Implicit function theorem.
» Conic sections in Cartesian coordinates, Plane polar coordinates and their use to represent the straight line and conic sections. Cartesian and spherical polar coordinates in three dimensions. The plane, the sphere, the ellipsoid, the paraboloid and the hyperboloid in Cartesian and spherical polar coordinates.
Section-C (20-marks)
III. Complex Variables
» Function of a complex variable; Demoiver’s theorem and its applications. Analytic functions, Cauchy’s theorem. Cauchy’s integral formula, Taylor’s and Laurent’s series. Singularities. Cauchy residue theorem and contour integration. Fourier series and Fourier transforms.
Suggested/Recommended Books:
Download PURE MATHEMATICS Past Papers Download PURE MATHEMATICS Books
Statistics CSS Syllabus:
Part – I (50 marks)
I. Descriptive Statistics
Definition, Importance and scope of Statistics, Descriptive and Inferential Statistics, Presentation of the Data, Tables, Graphs and Charts: Stem-and leaf diagram, Box and Whisker Plots. Measures of Central Tendency/location, Measures of Dispersion/Variability: Measures of Skewness and Kurtosis.
II. Basic Probability
Basic Probability Concepts, Additive and Multiplicative laws of Probability, Joint and Marginal Probabilities, Conditional Probability and Statistical Independence, Bayes’ rule. Concept of a Random Variable, Mathematical Expectations, Discrete and Continuous Random Variables, Probability Distribution, Mean and Variance of a Discrete Probability Distribution.
III. Probability Distributions
Discrete and continuous Probability Distributions. Properties, applications of Binomial, Poisson, Hyper-geometric distribution, Normal Distribution and its properties, Standard Normal Curve, Normal approximation to Binomial and Poisson distribution.
IV. Regression Analysis & Correlation Analysis
Concepts of Regression and Correlation and their application, Simple and Multiple Linear Regression (upto three variables), Estimation of the Parameters of simple regression Model, Method of least square, Inference regarding regression parameters. Correlation, Correlation Coefficient, Properties of Correlation Coefficient, Inference regarding correlation coefficient, Partial Correlation and Multiple Correlation Coefficients (upto three variables).
V. Non-Parametric Methods
Parametric versus nonparametric tests, when to use non parametric procedures, One-sample tests: Sign test, Wilcoxan signed ranks tests, Kolmogrov-Smirnov test, run test. Tests for two related samples: sign test, run tests, chi-square test, Test for two independent samples: Mann-Whitney test, Kolmogrov Smirnov test.
Part – II (50 marks)
I. Sampling & Sampling Distributions
Population and Sample, Advantages of Sampling, Sampling Design, Probability & Non-Probability Sampling techniques. Brief Concepts of Simple Random, Stratified, Systematic, Cluster, Multiphase and Multistage Sampling. Non-probability sampling: Purposive, Quota Sampling, Convenience & Accidental Sampling. Sampling with and without replacement, Application of Central Limit Theorem in Sampling, Sampling Distribution of Mean, difference between two Means, Proportion, difference between two Proportion and Variance.
II. Statistical Inferences
Estimation: Point Estimation, Properties of a good Estimator. Interval Estimation. Interval Estimation of Single Population means and Single proportion. Difference between two means and Difference between two proportions. Hypothesis Testing: Types of errors. Hypothesis Testing for Population Mean. Inferences for difference between Two Population Means. Inferences for the difference between Means of Two Normal Populations using Independent Samples (variances are assumed Equal) for sample size. Inference for Two Populations Mean using Paired Samples. Hypothesis testing for Single Population Proportion and difference between two population proportions. Estimation of sample size Analysis of categorized data. Goodness of fit tests. Contingency tables. Test of independence in contingency tables.
III. Design of Experiments
One-way and Two-way Analysis of Variance, Design of Experiments, Concepts of Treatment, Replication, Blocking, Experimental Units and Experimental Error, Basic Principles of Design of Experiments, Description, Layout and Statistical Analysis of Completely Randomized Design (CRD), Randomized Complete Block Design (RCBD), Multiple Comparison tests (LSD test).
IV. Population Analysis & Vital Statistics
Population and Demographic Methods, Sources of Demographic data, Basic Demographic Measures, Sex Ratio, Child Women Ratio, Vital Index, Crude and Specific Birth and Death Rates, Total Fertility and Net Reproduction Rates. Official Statistics: Statistical Systems in Pakistan, Functions of Statistics Division, Bureaus of Statistics and NADRA. The National Income, Gross Domestic Product, Saving and Wealth, Index Numbers.
Suggested Readings:
Download Statistics Past Papers Download Statistics Books
Geology Syllabus CSS (100 Marks)
Part- I (50-marks)
I. Introduction to Physical Geology
Introduction and scope of geology, its importance and relationship with other sciences; Earth as a member of the solar system: its origin, age, composition and internal structure; Introduction to rocks and minerals; Weathering and erosion; Isostasy; Geological Time Scale.
GEOLOGY Syllabus CSS
II. Stratigraphy and Palaeontology
Principles of stratigraphy; Laws of superposition and faunal succession; Geological time scale with divisions; Classification and nomenclature of stratigraphic units: lithostragraphic units, biostratigraphic units and chronostratgraphic units. Introduction to fossils and their significance; Modes of fossilization; Study of morphology, range and broad classification of major invertebrate phyla; Introduction to micro fossils; Introduction to Palaeobotany; Introduction and classification of major vertebrates; Introduction to micropaleontology GEOLOGY Syllabus CSS
III. Mineralogy
Classification of minerals; Study of internal structure; Polymorphism and isomorphism; Paragenesis; Physical and optical properties of the common silicate and non-silicate mineral groups; Introduction to crystallography: elements of symmetry, study; normal classes of crystallographic systems.
IV. Structural Geology and Tectonics
Stress-strain concepts; factors controlling the mechanical behavior of materials; Folds; Faults; Joints; Foliation: terminology, classification and relationship with bedding; Lineation; Unconformity. Plate tectonics theory; Geological evidences for continental drift; Sea-floor spreading; Oceanic ridges; Continental rifts; Intra-oceanic islands; Hot spot and Mantle plumes; Wilson Cycle; Tectonic framework of Pakistan.
V. Petrology and Petrography
Introduction, classification and description of sedimentary rocks; origin; transportation and deposition of sediments; Texture of sedimentary rocks; Sedimentary structures, their classification, morphology and significance; Composition, origin, differentiation and evolution of magma; Classification of igneous rocks; Mode of occurrences and types of extrusive rocks; Texture and structure of igneous rocks; Introduction to metamorphism; Types of metamorphism; Grades, zones and facies of metamorphism; Metamorphic diffusion and differentiation; Metamorphism in relation to Plate Tectonics; Differentiation between metamorphism and metasomatism. Introduction to Polarizing Microscope; Optical properties of opaque and non opaque minerals in plane polarized light and under crossed nicol including metallic under reflected light; Description of optical properties of common rock forming minerals.
Part- II (50-marks)
I. Introduction to Geophysics
Definition and relation of geophysics with other sciences; Classification and brief description of various branches of geophysics such as seismology, geomagnetism, geo[electricity, tectonophysics, gravimetry, geo-thermy and geodesy; Introduction to various geophysical techniques for exploration of mineral deposits, oil and gas, subsurface water and engineering works.
II. Sequence Stratigraphy
Introduction: history, concept and significance of sequence stratigraphy; Data sources: seismic reflections, outcrops, well logs, core and seismic facies; Sea level changes: their causes and effects, accommodation, eustatic and relative sea curve; Hierarchy of sequence stratigraphic elements; Types of sequences and systems tracts.
III. Petroleum Geology
The nature and classification of petroleum hydrocarbons, their origin, migration and accumulation; Source sediments, reservoir rocks and trapping mechanism for oil and gas; Prospecting and exploration of oil and gas; Reservoir: characteristics, drive mechanism, energy and pressure maintenance; Secondary and enhanced recovery; Introduction to Sedimentary Basins of Pakistan.
IV. Engineering and Environmental Geology
Rock and soil mechanics and its application in civil engineering; Rock mass characteristics; Geotechnical studies of rocks and soils; Geological factors and strength of rocks; Study of geological factors in relation to the construction of buildings’ foundations, roads, highways, tunnels, dams and bridges; Application of geophysical methods for site investigation; Construction materials; Mass movement: their causes and prevention. Introduction to environmental geology; Management of natural resources; Global climatic changes; Environmental controls for erosion, desertification and coastal degradation; Geological hazards such as floods, landslides, earthquakes, tsunamis, volcanoes, glaciers and shoreline processes; Remedial measures; Clean sources of energy; Industrial pollution, solid and liquid waste disposal, Introduction to environmental impact assessment and initial environmental examination.
V. Mineral and Energy Resources
Introduction of geological exploration/prospecting. Brief description of hydrocarbons, coal, gemstones, copper, lead, zinc, iron, gold, chromite, manganese, salt, gypsum, bauxite, sulphur, barite, fluorite, clays, phosphorite, building and dimension stones; Industrial rocks and minerals; Radioactive minerals and rocks; Special reference to economic mineral deposits in Pakistan. Origin, occurrence, and depositional environments of coal; Coal constitution and its kinds; Coal rank, grade and calorific value; Coal deposits of Pakistan with reference to Thar Coal; Geothermal energy resources of Pakistan.
VI. Economic and Applied Geology
Metallic and Non-metallic mineral resources of Pakistan; Mineral-based industries. Overview of Recodec Copper; Radioactive minerals and their occurrences in Pakistan; Gemstones of Pakistan. Geology of Reservoirs, dams, highways and tunnels; Major natural hazards and their impacts on the environment with special reference to Pakistan.
Recommended Books:
Download Geology Past Papers Download Geology Books
Group-III: (To select one subject of 100 marks only)
Business Administration CSS Syllabus:
I. Management
Defining Organization, Management, and Management in Organizations
Four Management Functions, Management Roles, Management Skills
Organizational Internal-External Environment
Management Planning, Goal Setting, and Decision Making
Strategic Management Process: Strategy Formulation and Implementation
Developing Organizational Structure and Design
Designing Adaptive Organizations
Managing Change and Innovation
Leadership and Motivation
II. HR Management
Role of Human Resource Management in Organizational Performance
Functions of HRM
Process and Methods of Job Analysis
Planning and Forecasting Personnel Needs
Recruitment and Selection
Training and Development
Performance Management and Appraisal: Methods and Processes
Establishing Strategic Pay Plans
Compensation and Benefits
Ethics, Justice, and Fair Treatment in HR Management
Labor Relations and Collective Bargaining
III. Financial Management
An overview of Financial Management Introduction and significance of financial markets, Differentiation between real assets and financial assets, Types of Financial Markets, Role of capital and money markets in economic development, Organizational goals and shareholder wealth maximization
perspective
Time Value of Money Cost of money and the factors effecting the cost, Interest rate fundamentals and determinants of market interest rate, Role of Time value of money in finance, Concept
of future value and present value, Making timelines, Annuities, Perpetuities and mixed stream of cash flows, with and without growth, Present value and future value of cash flow streams, Compounding Interest; discrete and continuous, Loan amortization
Analysis and Interpretation of Financial Statements Reading the financial statements, Horizontal and vertical analysis including common size, ratio, comparative and index number trend analysis, Forecasting financials for future decision making, Evaluating credit, management, profitability, risk etc using
financial statements
Risk, Return and Introduction to Pricing, Measures of Risks and return, Investment return and expected rate of return,
Standalone risk: standard deviation and coefficient of variation, Risk aversion and required rate of return, Portfolio risk: Diversifiable vs. Market risk, Security Market Line and CAPM, Calculating WACC, Discounting process for price determination, Relevant risk and return for valuation
Cash flow and Budgeting, Significance of budgeting, Making cash budgets, Making financial forecasts, Difference between profit and cash flow, Read and analyze Statement of Cash flow.
Capital Budgeting Significance of Capital budgeting, Cash flow calculations: incremental cash flows, Capital budgeting decision rules: NPV, IRR, MIRR, Return, Finding optimal capital structure, calculating appropriate discount rate, Capital Rationing
IV. Operations and Supply Chain Management
a. Operations Management
Operations & Productivity
Operations Management (OM) as one of the Three Core Functions in an Organization. Significance and contributions of OM in the field of management. Future trends in OM and differences between goods and services.
Operations Strategy in Global Environment Developing mission & OM strategies, Critical Success Factors (CSF), Aligning Core Competencies with CSF
Process Strategy, Four Process Strategies, Process Analysis and Design, Process Mapping, Flow Diagrams, Process Charts, Service process design, Process Re-engineering
Capacity Planning, Design & Effective Capacity, Capacity Cushion, Capacity considerations, Managing demand, Capacity Planning, Leading vs Lagging Strategies, Single & Multiple
Product Break Even Analysis for Capacity Planning
Location Strategies, Factors Affecting Location Decisions, Methods for Evaluating Location Alternatives, Factor Rating Method, Load-Distance Methods, Center of Gravity Method, Service location Strategy
Layout Strategies Types of Layout, Layout Design, Fixed Position Layout, Process- Oriented Layouts, Office Layout, Retail Layout, Assembly Line Balancing
Inventory Management, Role of Inventory in Operations, ABC analysis, Record accuracy, Cycle counting, Inventory Models, Fixed Period Systems, Continuous Review Systems, Basic EOQ
Inventory Model, Safety Stock, Service Level b. Supply Chain Management
Introduction to supply chain management and logistics management
What is supply chain management and logistics management, Objectives, Importance, Examples of supply chain management and logistics management, Decision phases in supply chains
Supply chain performance Achieving strategic fit, Challenges in achieving strategic fit, Supply chain cost, Supply chain quality, Supply chain lead time
Supply chain drivers, Facilities as a driver, Inventory as a driver, Information as a driver, Transportation as a driver, Sourcing as a driver, Pricing as a driver
Balancing supply and demand Bullwhip effect, Demand collaboration, Information sharing in supply chains, accurate
response strategy
Supply chain coordination Obstacles in coordination, Vendor managed inventory, Collaborative planning forecasting and replenishment, Managerial levers to achieve coordination
IT in supply chain management, Role of IT in supply chain management, Customer relationship management, Supplier relationship management, Risk management in IT, Supply chain IT in practice
V. Marketing
Introduction to marketing
Developing marketing strategies and plans
Scanning the marketing environment
Analyzing consumer markets
Market segmentation
Managing marketing information
Branding
Product life cycle
Pricing
Managing distribution channels
Integrated marketing communications
Download Business Administration Past Papers Download Business Administration Books
Public Administration CSS Syllabus:
I. Public Administration: Concepts, Approaches and Context
Definitions; Role and Scope of Public Administration in Society; Issues in Public Administration Theory and Practice: Democracy versus Bureaucracy, Politics versus Administration, Efficiency versus Equity; Core Values of Public Administration: Rule of
Law, Efficiency, Equity and Fairness, Responsiveness; Traditional Public Administration; New Public Management; New Public Service; Governance Approach to Public Administration; Islamic Concept of Public Administration; Historical roots of Public administration in Pakistan.
II. Public Administration: Classical and Contemporary Theories and Concepts
Bureaucracy; Scientific Management; Human Relations Approach; Leadership, Motivation, Network Governance; Strategic Management; Public Choice Theory; Types of Organizational Structure; Organization of Federal, Provincial, and Local Government in Pakistan; Administrative Culture of Pakistan; Inter-governmental Relations at Federal and Provincial level in Pakistan.
III. Public Policy Planning, Implementation and Evaluation
Strategic Planning and Management; Planning Process; Policy Analysis; Policy Implementation; Program Evaluation; Planning Machinery; Role of Donors and International Institutions in Public Policy and Management; Policy making and implementation in Pakistan.
IV. Budgeting and Financial Management
Budget as a Policy Tool; The Budget as a Managerial Tool; Principles of Budgeting, Audit and Accounting in Government; Line-Item Budgeting; Performance Budgeting; Program Budgeting; Zero-Base Budgeting; Outcome-Based Budgeting. Planning and Budgeting in Pakistan.
V. Managing Human Resources
Spoil system versus Merit System in Public Employment; Personnel versus Human Resources Management; Close system versus Open System of Public Employment; Functions of Human Resources Management; Implementation of HRM in Public
Sector: Key Issues and Challenges.
VI. Administrative Law
Meaning; Scope and Significance; Nature and Contents of Administrative Law, Administrative Ethics, Delegation of Authority and Legislation, Administrative Tribunals; Administrative Law in Pakistan.
VII. Public Management Skills
Planning; Decision Making, Conflict Management; Leading, Communication, Administrative Buffering; Managing Change; Managing Diversity; Stress Management; Delegation; Public Service Motivation; Creativity and Problem Solving; Issues of Public Management.
VIII. The Civil Service of Pakistan
Historical Background of Civil Service, The Structure of civil Service; History of Civil Service Reform; Management of Civil Service; Institutional and Cultural Context of Civil Service; Role of Civil Service in Good Governance, Gender and Civil Service.
IX. Organization of Provincial and Local Government
Governance Structure of Provincial Administration; Organization of Provincial Secretariat; Organization and Functions of Provincial Authorities and Agencies and their Relationship with Government Departments; Post-devolution Local Governance;
Organization and Functions of District Government and Administration; Organization and Structure of City District Government; Issues and Challenges of Local Governance.
X. Governance and Administrative Reforms
Theories of Administrative Reforms; Types of Administrative Reforms; Privatization; Regulation; De-regulation; Decentralization; Partnerships and Collaboration; Business
Re-engineering, Quality Assurance; Administrative Reform in Pakistan.
XI. Public Administration Accountability & Control
Bureaucratic Responsiveness; Representative Bureaucracy; Citizens Engagement in Public Service; Accountability & Control; Concept and Approaches to Public Accountability; Institutional Framework for Administrative Accountability; Legislative,
Executive and Judicial Control over Administration; Administrative Corruption; Role of Civil Society in Good Governance; Media, Interest Groups and Civil Society
Organizations; The Situation in Pakistan.
XII. Public Administration and Development
Role of Public Administration in Development; Concept of Development Administration; Difference Between Development Administration and Development Management; Changing Role of Public Administration in Development, Issues and Challenges of Public Administration in Pakistan.
Download Public Administration Past Papers Download Public Administration Books
CSS Governance and Public Policy Syllabus:
I. Basic Concepts of Governance:
Origin of the term Governance
Definition of Governance
Definition of Good Governance
Characteristics of Good Governance: Participation, Rule of law, Transparency, Responsiveness, Equity, Effectiveness and Efficiency, Accountability, Strategic Vision
Collapse/Failure of Governance: its indicators diagnostic tools & Effects
II. Governance Theories:
Communitarianism
Decentered Theory
Libertarian Socialism
Institutionalism
Marxism
Neoliberalism
Rational Choice Theory
Regulation Theory
III. Governance Indicators laid by World Bank/IMF/UNESCO/UNDP/ADB, their Explanation & Application Level in Pakistan:
Voice and Accountability
Political Stability and Absence of Violence
Government Effectiveness
Regulatory Authorities & their Quality
Rule of Law
Control of Corruption
IV. Public Policy and Planning Institutions and their role in Planning
Institutional Framework for Policy Coordination and Planning(ECNEC, Economic Coordination Committees of the Cabinet, The Federal Cabinet, The Secretaries Committee, The Prime Minister’s Secretariat, The Planning Commission, The
Finance Division, The Cabinet Division, and all Federal Ministries for their respective subjects)
Role of Planning Commission in Policy and Planning
Strategic Planning in Federal
Provincial Government and Local Government
Role of International Donors in Policy Formulation (IMF Document “Memorandum on Economic and Financial Policies 2013/14–2015/16,” that underpins almost all public policies.)
Public Policy and Implementation in Key Sectors (i.e., Health, Education).
V. Accountability:
General Introduction to Accountability and its concepts(Standards, Symbolism, regional and country-wide comparisons, a Review of Contemporary Studies)
Types of Accountability- Political Accountability, Legal/ Judicial Accountability, Administrative Accountability, Professional Accountability, Private vs. Public Accountability
National Strategies against Corruption and remedial measures.
VI. Bureaucracy:
Introduction to the Concept of Bureaucracy(History, Neutrality, Steel Frame of the State, Negative Connotations Associated with the term)
Theories of Bureaucracy (Max Weber, Marx, John Stewart Mill, Woodrow Wilson)
Role of Bureaucracy in Pakistan (British legacy, civil-military relations, neutrality, dilution of neutrality, political allegiance, power, corrupting the incumbent, institutional degradation, constitutional guarantees, indexing of salaries with the
CPI or lack thereof.)
Public Administration and Code of Ethics (Effectiveness of the Estacode and the Code of Ethics, Comparison with other countries)
VII. Public Policy Formulation and Implementation
The Policy Making Process: How Policies are Made (Six including diagnosis and six stages with cautions to be exercise at each stage)
Policy Implementation & Role of Bureaucracy (Training, Pervasive Inertia and how to break it, Lack of Decision Making, Culture of postponement and delays, Lack of resources, Political interference, Ability to say “No.”)
Policy Analysis, The Quest for Solutions (Lack of research in policy analysis, Lack of coordination among departments, secrecy, openness)
Policy Evaluation: Assessing The Impact of Public Policy, Program Evaluation- Success and failure of Govt.
VIII. Multi-level Governance in Pakistan:
Legislature: National Assembly, Senate, Provisional Assemblies
Judiciary: Supreme Court, High Courts, Lower Courts
Functioning of the offices:
President of Pakistan,
Prime Minister of Pakistan
Office of Governor,
Office of Chief Minister, Federal Cabinet, Cabinet Committees, Federal
Secretariat, Provincial Secretariat
Local Government system: District Government, Zila Government, Tehsil Government, Union Administration, Its Efficacy, Performance & Causes of Success or Failure
IX. Federalism, Devolution and Decentralization
Constituents participation in Federal Structure
Principle of Subsidiarity in Public Service Delivery
Decentralization Model of Kerala
X. Role of Citizens in Governance
XI. Good Governance in Islam
Quranic Guidance on Good Governance
Concept of Governance and its application in light of Quran; Sunnah and Fiqh.
Download CSS Governance and Public Policy Past Papers Download CSS Governance and Public Policy Books
CSS Town Planning and Urban Management Syllabus:
PAPER: TOWN PLANNING & URBAN MANAGEMENT (100 MARKS)
I. Definition of Town Planning, Goals and objectives of Town Planning: Town Planning as a multi-disciplinary approach and relationship of Town Planning with other professions.
II. Historical Perspective of Urban Planning: Planning of historical towns in the world. Examples of planned towns in Europe, Nile Valley region, Euphrates and Tigris Valley region and Indus Valley region (Mohenjodaro, Harappa, Kot Diji and Mehr Garh and Gandhara Civilization).
III. Urban Rural Differences and Hierarchy of Settlements: Urbanization and its effects on the environment of urban areas.
IV. History of planning in Pakistan: 5 year plans, Regional Plans, Master Plans etc.
V. Managing Urbanization
How to manage urbanization
Best Practices
Land use classification policy
Building and development control
Removal of encroachments
Introduction to Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS)
VI. Housing community and Economic Development: To prepare professionals with the skills and knowledge of equitable development. Commitment to expanding opportunities and providing quality of life for disadvantaged groups.
VII. Public Policy and Urban Design Management: Solving social and environmental problems using:
a. Economics,
b. Policy analysis,
c. Political science and
d. Urban Design
VIII. Sustainability, Environmental Policy and Planning:
How society conserves and manages its natural resources and works to promote development, while conserving and maintaining healthy environment.
IX. Urban Information Systems: Use of planning related software and spatial analysis tools and systems e.g. GIS, SPSS etc.
Download Town Planning and Urban Management Past Papers Download Town Planning and Urban Management Books
Group-IV: (To select one subject of 100 marks only):
HISTORY OF PAKISTAN and INDIA CSS Syllabus
I. Muslim Rule and Heritage in India (712-1857): Political History Arrival, foundation and consolidation of Muslim rule in India, important rulers of the Slave Dynasty and the Mughals. The Spirit and legacy of Muslim civilization, Art, Architecture and literature, Public Administration under Muslim Rules. Sultans, Kings, Economic, Social, Judicial, Civil and Military system during the Muslim rule, Industry, trade and commerce under the Muslim patronage, Financial Administration.
II. British Rule in India: 1857-1947: British Imperialism, origin and growth of the East India Company, Causes and effects of downfall of the Mughal Empire in India, War of Independence in 1857:Causes and effects.
III. Constitutional and Political Reforms of the British Government (1858-1947) and growth of the Political Parties Indian Congress
IV. Muslim Struggle for Independence: Role of Shah Wali Ullah, Syed Ahmad Shaheed and Sir Syed Ahmed Khan towards regeneration of the Muslim of South Asia, All India Muslim League, Partition of Bengal, Simla Deputation, Lucknow pact; Khilafat movement. Nahru Report Quaid-i- Azam’s Fourteen Points.
V. Pakistan Movement: Allama Iqal’s Allahabad Address 1930, and Round Table Conference. The Congress Rule in the provinces-1937-1939, Lahore Resolution 1940, various Missions and Plans for the partition of the South Asia. Founders of Pakistan: Quaid-i-Azam, Mohsin-ul-Mulk, Syed Amir Ali, Ali Brothers. Sir Agha Khan, Chaudhry Rehmat Ali, etc.
VI. History of Pakistan (1947- Todate): Pakistan’s early Challenges—Quaid-i-Azam as Governor-General, various attempts at constitution making.
VII. Military in Politics: Ayub Khan, Yahya, Zia–ul–Haq and Pervaiz Musharaf regimes, Civil Military Relationship in Pakistan,
VIII. Separation of East Pakistan: Causes and Effects,
IX. Working of Democracy in Pakistan: Liaquat Ali Khan to Firoz Khan Noon (1947-1958), Zulfiqar Ali Bhutto’s Period (1971-1977),Benazir, Nawaz Sharif ,Revival of Democracy: 1988 1999, Restoration of Democracy (2008 to date), Role of Major Political Parties and Pressure Groups in the history of Pakistan.
X. Foreign Policy of Pakistan (1947-1999)
Download History of Pakistan and India Past Papers Download History of Pakistan and India Books
Islamic History and Culture CSS Syllabus:
Part –I (Marks 50)
I. Pre-Islamic Near East: An Overview
Political, Social, Cultural, Religious and Economic Conditions in the Near East including Arabia before the dawn of Islam
II. The Dawn of Islam: The Prophetic Age (570-632)
Biography of the Prophet Muhammad (PBUH): A Chronology of the Major Events in his Life
Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) as a Motivator (Daa’i), Major points of his mission
Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) as a Military Leader/Strategist
Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) as a Political Leader/Head of the State
III. The Pious Caliphate (632-660)
Caliph Abu Bakr (632-34): Apostasy Wars and Consolidation of Islam
Caliph Umar b.Khattab (634-44): Establishment of Administrative System and Expansion of Muslim Empire
Caliph Uthman b.Affan (644-56): Problems and Issues in the Muslim Community
Caliph Ali b.Talib (656-660): Rise of Factionalism
Abdication of Imam Hasan and Establishment of Umayyad Dynasty (660)
IV. Political System of Islam under the Prophet (PBUH) and the Pious Caliphate
Nature of Islamic State
Form of the Government
Functions of the Islamic State
Sovereignty of God
Caliphate or Vicegerency of Man
Appointment of Caliph
Shura or the Consultative Body and its Role
V. Institutional Development of the Muslim Civilization: The Early Phase (622-660)
Development of Law and Judiciary in Early Islam
Administration and State Conduct
Defense in Early Islam
Educational System
Propagation of Islam
Financial Administration
VI. The Umayyads in Power (660-749)
Political History of the Umayyad Dynasty
Statecraft and Administration under the Umayyads
Society and the Development of Arabic Literature.
Cultural Achievements
Part –II (Marks 50)
I. The Abbasids of Baghdad (749-1258)
The Abbasid Revolution and the Establishment of the Abbasid Dynasty
Administrative Structure under the Abbasids
Development of Scientific Knowledge under the Abbasids
Muslim Philosophy under the Abbasids
Cultural Achievements
II. Spain under the Muslim Rule
Spain under the rule of the Arabs and Moors (711-1492)
Political Fragmentation and the Fall of Granada (1492)
Muslim Contribution in the Realm of Culture, Arts and Architecture
III. The Crusades against Islam
Major Encounters and Actors (1092-1228)
Impact of the Crusades on Muslim-Christian Relations
IV. The Ottoman Empire
Rise and Fall of the Ottoman Turks (1299-1923)
State, Society and Economy under the Ottomans
Treatment with the Religious Minorities
Contribution towards Culture, Arts and Architecture
V. Sufism as an Institution of the Muslim Society
Origin and Development of Sufism
Contribution of the Sufis to the Muslim Civilization
Relationship of the Sufis with the State and Political Authorities.
A Critical View of Sufism
VI. Islam and Modernity in Contemporary World
The Emergence of Islamic Modernism
Intellectual, Political, Economic, Social and Educational Aspects of Islamic Modernism
Dissemination of Muslim Learning in the West
Download Islamic History and Culture Past Papers Download Islamic History and Culture Books
British History CSS Syllabus:
Part –I (Marks 50)
I. The Glorious Revolution (1688)
Causes, and Results
William III and Mary II (1689-1702)
Queen Anne (1702-1714)
II. Hanoverian Era (1714-1790)
Jacobite Rebellions (1715 and 1745)
Robert Walpole and Whig Oligarchy
American War of Independence (1776)
III. The Union of England and Scotland
IV. Union of England and Ireland
V. The Old Colonial system
VI. The French Revolution and Napoleonic Wars
Causes
Britain and Napoleonic Wars
Impact on Britain
VII. Industrial and Agricultural Revolution
Causes
Effects on Political and Social Life of Britain
Party Politics
The Methodist Movement
Socialism
Liberalism
Colonization
Chartest Movement
VIII.Robert Peel and return of Torries
Internal policies
Irish Problem
IX. Victorian Era (1837-1901)
Internal Reforms
Liberals
Foreign Policy
Disraeli, Gladstone and Problems in Ireland
Great Britain and Free Trade
X. Edwardian Era (1901-1910)
Domestic and Foreign Policies (1901-1910)
The Origins of Labor Party
XI. Britain, World War I and its Aftermath
Causes
Britain and Peace settlement
Effects of War on Britain
League of Nations
The Great Depression
Appeasement and Rearmament
Part –II (Marks 50)
XII. Britain ,World War II and its Aftermath
Causes and events
Churchill, War Conferences
Creation of U.N.O
Effects of war
Reforms of Labour Government
XIII. Great Britain and Cold War
Creation of Common Wealth
NATO
Decolonization of the British Empire
Internal Policies and EEC
Foreign Policy
XIV. Thatcherism to Cameron (1979-2012)
Internal Policy
Society and culture
Foreign Policy
Falkland War
John Major and his Policies
European Common Market and the Great Britain
Formation of EU
Tony Blair “New Labour” Economic Crunch, War on Terror and his Policies
Global Financial Crisis 2008 and the Great Britain
Reforms under Cameroun
SUGGESTED READINGS
Download British History Past Papers Download British History Books
European History CSS Syllabus:
Part –I (Marks 50)
I. The French Revolution and Napoleonic Era (1789-1815)
The causes of French Revolution
The consequences of Revolution
Napoleon rise to power
Creation of Empire
The Continental system
The fall of Napoleon
II. The Concert of Europe (1815-1830)
The Congress of Vienna
Metternich’s Era
The Concert of Europe and Congress System
Balance of Power
III. Forces of Continuity and Change in Europe (1815-1848)
Nationalism
Liberalism
Romanticism
Socialism
Industrial Revolution
Colonialism
Consequences
IV. The Eastern Question (1804-1856)
The nature of the Eastern question
The Crimean War
Russo Turkish War 1877
Consequences
V. Unification of Italy
The effects of the revolution of 1848
The obstacles to unification
Cavour and the unification of Italy
The Process of Italian unification (1859-1871)
VI. Unification of Germany
The rise of Bismarck
Diplomatic events
The Austro-Prussian War (1866)
The Franco- Prussian War (1870-1871)
The triumph of Bismarck and process of unification
VII. The Origins of First World War (1890-1914)
Formation of Alliances and Counter Alliances
The Balkans War (1912-1913)
The outbreak of the World War 1
Part –II (Marks 50)
VIII. The First World War and its aftermath
The War (1914-1918) and peace treaties
The League of Nations
IX. Dictatorships in Europe
Fascism in Italy under Musssolini
Hitler, Nazism and Germany
Russia , Marxism Revolution and its working under Stalin
Great Depression and its effects on Europe
Appeasement
The Arm race
The Sudetenland Crisis (1938)
The distraction of Czechoslovakia (1939)
X. The Second World War and its Effects on Europe
The Main Events of the War
Impact of war
XI. Post- War Europe
The post war settlements
The United Nations
Economic Recovery of Europe, Marshal Plan
German Question
NATO
Decolonization
XII. Cold War Europe (1955-1991)
Effects of cold war
Warsaw Pact (1955)
The European Economic Community (EEC)
Nuclear Non-Proliferation Agreement
Charles de Gaulle and France
Spread of communist regimes in Europe
XIII. Europe (1991-2012)
The Gorbachev and Disintegration of USSR
The reunification of Germany
The Balkan crisis of 1990s
The European Union
Role of Europe in War against terrorism
Global Economic Crisis and Europe
Suggested Readings
Download European History Past Papers Download European History Book
History of USA Syllabus CSS:
I. Introduction:-
From ancient times to 1492
Advent of the Europeans to British supremacy (1492-1606)
II. USA as a British Colony (1606-1783).
III. USA as an Independent Country (1783 – 1819)
IV. Expansion of USA: From 13 to 50 States (1820 – 1949)
V. Constitution of the USA: Salient Features
VI. Civil War between the North and the East (1850 – 1869)
VII. Industrialization and its emergence as one of the world powers (1870 -1916)
VIII. USA’s role in the Two World Wars (1914 – 1918 & 1939 – 1945)
IX. Post 1945 world scenario and emergence of USA and USSR as the Two World Powers.
X. American Role in patronizing UNO and International Organizations 1945 – 2012
XI. American Role in Cold War and its emergence as the Sole Super Power (1945 -1990).
XII. International Concerns of USA: An Overview.
XIII. The War on Terror: The Role of Pakistan and USA (2001 – 2012)
XIV. Global perceptions of the USA.
XV. Progressive Era: Reforms of Theodore Roosevelt and Woodrow Wilson,
XVI. The Great Depression and the New Deal
XVII. Civil Rights Movement
XVIII. United States’ role in International Conflicts
XIX. US Presidential Election
XX. The US Congress: Role and Functions
XXI. Separation of Powers: Check and Balances
Download US History Past Papers Download US History Books
Group-V: (To select one subject of 100 marks only)
CSS Gender Studiesc Syllabus:
I. Introduction to Gender Studies
Introduction to Gender Studies
Difference between Gender and Women Studies
Multi-disciplinary nature of Gender Studies
Autonomy vs. Integration Debate in Gender Studies
Status of Gender Studies in Pakistan
II. Social Construction of Gender
Historicizing Constructionism
Problematizing the category of “Sex”: Queer Theory
Is “Sex” socially determined, too?
Masculinities and Femininity
Nature versus Culture: A Debate in Gender Development
III. Feminist Theories and Practice
What is Feminism
Liberal Feminism
Radical Feminism
Marxist/Socialist Feminism
Psychoanalytical Feminism
Men’s Feminism
Postmodern Feminism
IV. Feminist Movements
Feminist Movements in the West. First Wave, Second Wave and Third Wave Feminism. United Nation Conferences on Women, Feminist Movements in Pakistan.
V. Gender and Development
Colonial and Capitalistic Perspectives of Gender
Gender Analysis of Development Theories; Modernization Theory, World System Theory, Dependency Theory, Structural Functionalism.
Gender Approaches to Development: Women in Development (WID), Women and Development (WAD), Gender and Development (GAD); Gender Critique of Structural Adjustment Policies (SAPs).
Globalization and Gender
VI. Status of Women in Pakistan
Status of Women’s health in Pakistan
Status of Women in Education
Women and Employment
Women and Law
VII. Gender and Governance
Defining Governance
Suffragist Movement
Gender Issues in Women as Voters
Gender Issues in Women as Candidates
Gender Issues in Women as Representatives
Impact of Political Quota in Pakistan
VIII. Gender Based Violence
Defining Gender Based Violence
Theories of Violence against Women
Structural and Direct Forms of Violence
Strategies to Eliminate Violence against Women
IX. Case Studies of:
Mukhtaran Mai
Mallala Yousaf Zai
Shermin Ubaid Chinoy
Download Gender Studies Past Papers Download Gender Studies Books
Environmental Science CSS Syllabus:
I. History of Environmental Thought
Environment and Sustainable Development, History of Environmental Movements, Industrial and Agriculture Revolution, United Nations Conference on Human Environment 1972, Our Common Future 1987, Rio Summit 1992, Agenda 21, World Summit on Sustainable Development 2002, Rio Summit II, 2012, Millennium Development Goals.
II. Sustainable Development Issues
Population growth, Poverty, Biodiversity loss and its Conservation, Energy security (energy conservation and alternative energy resources), Urbanization and sustainable cities, Carrying capacity and ecological footprint. Food security and sustainable agriculture. Ecological restoration.
III. Interdisciplinary nature of Environmental Science
Orientation on convergence of various social and natural sciences to evolve a new discipline of environmental science: Environmental Biology, Environmental Chemistry, Environmental Physics, Environmental Microbiology, Environmental Toxicology, Environmental Economics, Environmental Geology, Environmental Geography, Environmental Biotechnology, Environmental Sociology.
IV. Environmental Pollution
Air Pollution, Water Pollution, Soil Pollution, Noise Pollution, Solid Waste, Water Logging & Salinity, Deforestation, Desertification, Eutrophication, Global and regional air pollution problems (Greenhouse effect, Global Warming/Climate Change, Ozone Depletion, Acid Rain).
V. Climate Change
Climate Pattern at local, regional and global scale. Different types of climate including tropical and mid latitude climate, polar climates. Climate change processes, Drivers and Indicators of Climate Change, Effects of Climate Change on natural and societal systems. Carbon foot print. Climate change adaptation and mitigation, Clean Development Mechanism (CDM), REDD+. Global environmental politics on climate change: role of India, China and USA (Copenhagen Accord 2009).
VI. Environmental Governance
Policy, legal and institutional frameworks for governance of environment in Pakistan: National Conservation Strategy of 1992, National Environmental Policy Act of Pakistan 2005, Environmental Protection Act of 1997, Pak-EPA (Review of IEE/EIA) Regulations 2000, Hospital Waste Management Rules 2005, Pollution Charge Rules, Sample Rules, Solid Waste Management Plan 2005, Hazardous Substances Rules 2005, National Drinking Water Policy 2009, Sanitation Policy, National Climate Change Policy 2012.
VII. Global initiatives
Brief on some of the Multilateral Environmental Agreements ratified by Pakistan, Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), Cartagena Protocol on Bio-safety, Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES), Convention on Wetlands of International Importance Especially as Waterfowl Habitat (Ramsar Convention), Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species (CMS), United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), Kyoto Protocol to UNFCCC, Montreal Protocol on Substances that deplete the Ozone Layer, United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD).
VIII. Environmental Assessment and Management
Environmental Impact Assessment, Strategic Environmental Assessment, Environmental Management Systems (ISO 14000), Occupational Health & Safety management systems (OHSAS 18000), Participatory Approaches to Environmental Management, Technological Approaches to Environmental Management, Approaches to Solid Waste Management, Disaster Risk Management, Pollution Control Technologies, Geographic Information System & Remote Sensing, Natural Resources Management.
Download Environmental Science Past Papers Download Environmental Science Books
Botany CSS Syllabus:
I. Algae, Fungi and Bryophytes
Phycology: Distribution, Classification, Structure, Life History and Economic importance of the main groups of Algae.
Mycology and Plant Pathology: Structure, Reproduction, Classification and Economic importance of the main groups of Fungi. Diseases of economically important crops and general principles of their control
Bryology: Structure and reproduction of bryophytes, Evolution of Gametophyte and Sporophyte.
II. Pteridophyta and Gymnosperms
General account with special reference to structure, life history and affinities of both Pteridophytes and Gymnosperms. Ontogeny and structure of seed, classification and economic importance of Gymnosperms.
III. Anatomy and Embryology
Primary and secondary tissues. Meristems. Secondary growth in dicot stem. Anatomy of leaf, stem and root.
Micro and megasporogenesis, pollination mechanism, fertilization, development of Embryo and Endosperm, Seed dispersal.
IV. Taxonomy of Angiosperms
Systems of classification. Rules of botanical nomenclature. Concepts of speciation. Introduction to modern trends in plant taxonomy: bio-systematic, chemotaxonomy and numerical taxonomy. General characters and economic importance of common angiosperm families.
V. Plant Physiology
Plant water relations, Osmotic Quantities, component potentials of water and their role in transport, water absorption by roots, transpiration. Role of essential mineral elements and their uptake. Plant hormones. Photoperiodism, Vernalization. Dormancy and Seed germination Enzymes.
Photosynthesis: Plant pigments, Light reaction, CO2 fixation, Mechanism of photophosphorylation.
Respiration: Glycolysis, Kreb cycle, Mechanism of oxidative phosphorylation.
VI. Ecology
Influence of climatic, edaphic and biotic factors on plant growth. Vegetation sampling techniques. Concepts of ecosystems and their productivity, ecological energetics, Pyramids (of numbers, biomass and energy), trophic levels, food chains and food webs. Biogeochemical cycles (Hydrological and Nitrogen).
Succession.
Causes and reclamation of soil salinity and water logging in Pakistan. Soil erosion, its control and soil conservation methods. Deforestation. Biodiversity conservation Pollution.
VII. Cytology
Cell cycle, cellular morphology, chemistry of cell wall and cell membrane, cell to cell communication, plant tissue and cell culture, cell senescence and cell death.
Ultra-structure of various cell organelles: Mitochondria, Golgi bodies, Endoplasmic reticulum, Plastids, Ribosomes, Glyoxysomes, Vaculoes, Nucleus.
VIII. Genetics
Mendelian Genetics, Multiple Alleles, Polygenic inheritance, Gene interaction, Epistasis and pleiotropy, Sex-linked inheritance, Chromosomal aberrations, Mutations, DNA repair.
IX. Evolution
Introduction of Evolution, Evolutionary history, Evolution of life, Convergent Evolution, Divergent Evolution, Parallel Evolution and Natural selection
X. Molecular Biology
Nucleic acids, DNA as hereditary material, DNA replication, Transcription, Genetic code, Protein synthesis, Genetic engineering and its application, Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO).
SUGGESTED READINGS
Download CSS Botany Past Papers Download CSS Botany Books
Agriculture and Forestry Syllabus CSS:
Part-I: Agriculture (50 marks)
I. Concept of Integrated Agriculture: Components of natural resources as bases for agriculture production (Land, Water, biological, Environmental, Solar, Energy)
II. Challenges in Pakistan’s Agriculture: Present scenario and future prospects. Analytical overview: issues and strategies for improvement of crop management, livestock management, fisheries, cottage industry, resource management and rural development. Institutions and policies: issues and options.
III. Elements of Climate and their Relationship with Crop Growth: Farming Systems, biological nitrogen fixation, soil profile, structure and texture, soil fertility, soil erosion and conservation, water logging and salinity
IV. Genetic Improvement for Crop Production: GMO crops, Seed production technology.
V. Horticulture: Floriculture, landscaping, pests and diseases of agriculture crops and their control, integrated pest management.
VI. Rainfed and Irrigated Agriculture: Agriculture mechanization, land tenure and land reforms, role of agriculture in national economy.
Part-II Forestry = (50 Marks)
I. Forest, rangelands and wildlife importance and significance
II. Forest management and utilization, wood based industries in Pakistan, silviculture
III. Range management and utilization
IV. National and international forest wealth statistics
V. Role of wildlife as value addition to forestry
VI. Forest based wildlife resources of Pakistan and their management, eco-tourism
VII. Forestry, agroforestry, social forestry and forest biometrics
VIII. Socio-economic and ecological impact of man made forests
IX. Watershed Management and role of forests in prevailing climate change dilemma
X. National forest laws and policies at national level, biodiversity & environment
SUGGESTED READINGS
Download Agriculture & Forestry Past Papers Download Agriculture & Forestry Books
CSS Zoology Syllabus:
I. Animal Diversity-Invertebrates
Architectural pattern of an animal, Taxonomy and phylogeny, Major subdivisions of animal kingdom.
Animal-Like Protists: The Protozoa: evolutionary perspective, locomotion and reproduction, Protozoa of veterinary and medical importance.
Porifera: Body wall, skeleton and water currents system. Coelenterates: Reproduction plan and alteration of generation (Polymorphism), Coral reefs.
Platyhelminthes and Nematodes: Parasitic adaptations and medical importance. Annelids: Metamerism and ecological importance.
Molluscs: Modification of foot, Feeding and their role in the shell fishery.
Arthropods: Modification in their mouth parts, Role of arthropods as vectors in the transmission in microbial infection. Arthropods and their ecological importance.
Echinoderms: Characteristics, Evolutionary perspective, Relationships to other animals; echinoderm characteristics.
II. Animal Diversity-Chordata
Hemichordates and Invertebrate Chordates: Evolutionary Perspective: Phylogenetic Relationships and considerations.
Fishes: Structural and functional adaptations of fishes.
Amphibians: Movement onto land and early evolution of terrestrial vertebrates.
Reptiles: Characteristics of reptiles, adaptations in reptilians.
Birds: Migration and navigation, adaptations.
Mammals: Structural and functional adaptations of mammals.
III. Principles of Animal Life
The chemical basis of animal life: Brief introduction to bio-molecules; carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids.
Cell concept and cell theory, Organization of cellular organelle (their structure and functions), Central dogma of cell biology (Transcription and Translation), Meiosis and Mitosis
Protozoa: Reproduction pattern in protozoan, Parasitism in protozoan
Mesozoza and Parazoa: Porifera: Cells types, body wall and skeleton and water currents system, Coelenterata: Reproduction plan and alteration of generation (Polymorphism)
Tissues Types: epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous tissues; organs and organ systems.
Enzymes function and factors affecting their activity, cofactors and coenzymes.
Energy Harvesting: Aerobic and anaerobic respiration the major source of ATP.
Mendel’s law of inheritance, Chromosomal basis of inheritance, Multiple alleles, Eukaryotic chromosomes: Mutations and chromosomal aberrations.
Ecological Concepts: Interactions, Concepts and components of ecosystem, Food chain, Food web, Biogeochemical cycles, Forests, Biomes, Wildlife conservation and management, Environmental pollution, Green house effect, Acid rain, Global warming and climate change.
Evolution: Darwinian evolutionary theory based on natural selection and the evidence, Microevolution: Genetic variation and change within species, Macroevolution: Species and speciation (Allopatric, Parapatric and Sympatric speciation)
IV. Animal Form and Function
Protection, Support and Movement: Integumentary system of invertebrates and vertebrates; Animal muscles: the muscular system of invertebrates and vertebrates.
Digestion and Nutrition: Feeding mechanism, Digestion, Organization and regional function of alimentary canal, Regulation of food intake, Nutritional requirements
Internal Fluids and Respiration: Internal fluid environment, Composition of blood, Circulation and respiration mechanisms
Homeostasis: Excretion, Vertebrate kidney mechanisms, Temperature regulation
Nervous Coordination: Nervous system and Senses: Functional units of nervous system, Synapses junctions between nerves.
Chemical Coordination: Endocrine System; Vertebrate endocrine glands and types of hormones, Mechanism of hormones action,
Animal Behavior: Learning, Habituation, Insight learning, latent learning, classical learning: Control of Behavior; social behavior
Download CSS Zoology Past Papers Download CSS Zoology Books
English Literature CSS Syllabus:
The paper is divided into six components along with the marks allocation for each component.
I. Essays: (10 Marks)
Bertrand Russell (The Conquest of Happiness)
George Orwell (Politics and the English Language; The Prevention of Literature)
Ralph Waldo Emerson (The Transcendentalist; Self-Reliance)
II. Short Stories: (10 Marks)
Somerset Maugham (The Lotus-Eater)
G.K.Chesterton (A Somewhat Improbable Story)
O’Henry (The Gift of the Magi)
III. Poetry: (20 marks)
William Wordsworth (Resolution and Independence; Lines Composed Few Miles Above, Tintern Abbey)
John Keats (Ode to a Nightingale; Ode to Autumn)
Lord Alfred Tennyson (Ulysses; The Lady of Shalott)
Yeats (A Dialogue of Self and Soul; The Second Coming)
Eliot (The Wasteland; Love Song of J. Alfred Prufrock)
Philip Larkin (Maturity; Continuing to Live; The Trees)
Wallace Stevens (A Postcard from the Volcano; Continual Conversation with a Silent Man; Dry Loaf) OR Walt Whitman (As I Ponder’d in Silence; Are You the New Person Drawn Toward Me?; This Moment Yearning and Thoughtful)
IV. Drama: (20 marks)
Shakespeare (Hamlet; King Lear; Twelfth Night)
William Congreve (The Way of the World)
Shaw (Pygmalion; Heartbreak House )
Harold Pinter (The Caretaker)
Samuel Beckett (Waiting for Godot)
Eugene O’Neill (Long Day’s Journey into Night)
V. Novels: (20 marks)
Thomas Hardy (Far from the Madding Crowd)
D.H. Lawrence (Sons and Lovers)
George Orwell (Nineteen Eighty-four)
James Joyce (A Portrait of the Artist as a Young Man)
Iris Murdoch (Under the Net)
Nathaniel Hawthorne (The Scarlet Letter) or William Faulkner (The Sound and the Fury)
VI. Literacy Theory & Criticism (20 Marks)
Structuralism
Marxism
Deconstructionism
Psychoanalytic criticism
Feminist criticism
Postcolonial Criticism
Note: The texts are mentioned in brackets in front of each author’s name. However, for the component on “Literary Theory and Criticism” and for understanding poetry and drama,
particularly 20th century poetry and Drama, following readings are suggested:
Download English Literature Past Papers Download English Literature Books
Urdu Literature CSS Syllabus:
Download Urdu Literature Past Papers Download Urdu Literature Books
Group-VI: (To select one subject of 100 marks only)
LAW Syllabus CSS
I. Definitions of Crime
II. All Provisions of:
i. Concept of arbitration, arbitration with or without intervention of court and in civil suits.
ii. Establishment of Civil Courts with their Original & Appellate Jurisdiction.
iii. The Code of Civil Procedure, 1908
iv. Pakistan Penal Code, 1860
v. Qanun-e-Shahadat Order, 1984
vi. Criminal Procedure Code, 1898
Download CSS Law Past Papers Download CSS Law Books
Constitutional Law CSS Syllabus:
I. Definition and Scope of Constitutional Law, Basic Constitutional Concepts (Constitutional Conventions, Rule of Law, Due Process), Constitutional Structures (Parliamentary, Presidential, Separation of Powers), Judiciary (Independence of
Judiciary, Judicial Review, Theories of Constitutional Interpretation)
Fundamental Human and Political Rights and Civil Liberties (freedom of speech, association, assembly, movement and Right to Counsel, life, property, religion, privacy, self incrimination, double jeopardy).
II. Principles of Constitutional Law with special reference to United Kingdom, United States of America, France, Russia, China, Pakistan, India and Turkey.
III. Constitutional History of Pakistan: Principles of Constitutional Law of Pakistan, Salient feature of the Government of India Act, 1935, Indian Independence Act 1947, Objectives Resolution 1949,
Constitutions of 1956, 1962 and 1973, Abrogation and Suspension of the Constitutions and the Martial Laws, Legal Framework Order, 1970, The PCO of 1981, The RCO of 1985, The LFO-2002, Amendments in the 1973 Constitution.
IV. Legal Development:
Maulvi Tamizuddin Khan v. Federation of Pakistan PLD 1955 Sindh 96.
Federation of Pakistan vs. Maulvi Tamizuddin Khan, PLD 1955 FC 240
Reference by the Governor-General PLD 1955 FC 435
State v. Dosso PLD 1958 SC 533.
Usif Patel v. Crown PLD 1955 FC 387
Begum Nusrat Bhutto v. Chief of the Army Staff PLD 1977 SC 657
Hakim Khan v. Government of Pakistan PLD 1992 SC 595
Nawaz Sharif v. President of Pakistan PLD 1993 SC 473
Benazir Bhutto v. the President of Pakistan PLD 1992 SC 492
Khawaja Muhammad Sharif, PLD 1988 Lah. 725
Federation of Pakistan v. Haji Saifullah Khan PLD 1989 SC 166
Khawaja Ahmad Tariq Rahim PLD 1992 SC 646
Benazir Bhutto v. President of Pakistan, PLD 1998 SC 388
Asma Jilani v. Government of the Punjab PLD 1972 SC 139
State v. Zia ur Rehman PLD 1973 SC 49
Mahmood Khan Achakzai v. Fed. of Pakistan PLD 1997 SC 426
Zafar Ali Shah v. General Pervez Musharraf, PLD 2000 SC 869.
Sindh High Court Association v. Federation of Pakistan, PLD 2009 SC 879.
Download Constitutional Law Past Papers Download Constitutional Law Books
CSS International Law Syllabus:
I. Nature, Origin and Basis of International Law.
The Emergence of International Law, Early European Authors, The Nation-State System, The Enforcement of International Law, The Effectiveness of International Law, The Weakness of International Law, The Juridical Basis of International law,
The Future of International law and Material Sources of International Law.
II. Relation between International Law and State Law.
Article 38 of the Statute of International Court of Justice, Primary Sources of International Law, Subsidiary Sources of International Law, International Soft Law
III. State in General and Recognition
Personality and Statehood in International Law, The Subjects of International Law, Recognition of State and Government in International Law, Recognition of State and Government in National Law.
IV. The Law and Practice as to Treaties
The Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties
V. The Settlement of International Disputes.
Negotiation, Mediation and Good Offices, Inquiry, Settlement by the United Nations, Conciliation, Arbitration, The International Court of Justice.
VI. International Humanitarian Law.
International and Non-International Armed Conflicts, Non-International Armed Conflict, ‘Combatant’ and ‘Protected Persons’, Protection of Wounded, Sick and Ship-Wrecked Persons, POWs, Civilians, Limitations on the Conduct of War, Limits on the Choice of Methods and Means of Warfare.
VII. The Use of Force
The Law before the UN Charter, The Law after the Charter, The Collective Use of Force, The Right of Self-Defence.
VIII. International Institutions
IX. State Territorial Sovereignty.
X. State Responsibility.
XI. State Jurisdiction.
XII. Succession to Rights and Obligations.
XIII. The State and the Individual.
XIV. The State and the Economic Interest.
XV. Diplomatic Envoys, Counsels and other Representatives.
XVI. War, Armed Conflicts and other Hostilities.
XVII. Neutrality.
Download International Law Past Papers Download International Law Books
Muslim Law and Jurisprudence CSS Syllabus:
I. The Sources of Islamic Law
The Quran
The Sunnah
Ijma
Qiyas
Ijtehad
II. Principles of Islamic Jurisprudence
III. Islamic Criminal Law
Hadd
Taz’ir
Qisas and Diyat
IV. Islamic Family Law
Marriage
Dower
Divorce
Separation by Repudiation (Talaq)
Separation by Mutual Agreement (Khula)
Judicial Separation (Faskh)
Post-Divorce Maintenance
Child Custody
Succession
V. Islamic Law of Contract
VI. Islamic Banking and Insurance
VII. Islamic International Law
VIII. Islamic Law and Human Rights
IX. Dissolution of Muslim Marriages Act, 1939
X. Muslim Family Laws Ordinance 1961
Download Muslim Law & Jurisprudence Past Papers Download Muslim Law & Jurisprudence Books
Mercantile Law CSS Syllabus:
I. Law of Contract, 1872. ![]()
Definitions
Essentials of a valid contract (Proposal, Acceptance, Consideration, Free consent, Capacity of Parties, Not hereby declared to be Void)
Kinds of Contracts (Valid, Void, Voidable, Not Voidable)
Variety of Contracts (Contingent, Quasi, Bailment, Pledge, Indemnity, Agency)
Performance of Contract, contracts that need not to be performed.
Breach of contract, consequences of breach, damages for breach of contract.
II. Sales of Goods Act, 1930
Definitions
Differences: Sale & agreement to sell, conditions and warranties, express & implied conditions.
Doctrines: Caveat emptor, Nemo dat
Right and duties of seller & buyer, rights of unpaid seller.
III. Partnership Act, 1932
Definitions
Essentials of partnership
Kinds of partnership (partnership at will, particular partnership, limited partnership)
Rights and duties of Partners
Relation of partners to third persons (implied authority of partner, doctrine of holding out)
Incoming and outgoing partners (minor)
Dissolution of firms (compulsory, by agreement, by court, by notice on happening of contingencies)
IV. Negotiable Instrument Act, 1881
Definitions
Types of negotiable instruments (Cheque, bill of exchange, promissory note)
Parties to instruments, holder & holder in due course
Rules (as to negotiation, presentment, payment & interest, discharge, noting and protest, compensation, acceptance, payment for honour)
Special rules of evidence
Special provisions relating to cheques & bills of exchange (dishonor, duties of banker)
Provisions as to foreign instruments
V. Competition Act, 2010
Definitions
Prohibition and abuse of (dominant position, certain agreements, discipline, marketing practices)
Approval of mergers
Competition commission of Pakistan (established, composition, term)
Functions and powers of commission
Provisions as to penalty and appeals.
VI. Electronic Transaction Ordinance, 2002
Definitions
Recognition and presumption of electronic transactions (writing, signature, stamp duty, attestation etc.)
Electronic documents (attribution, acknowledgement, time and place of dispatch)
Certification of service providers
Application to acts done outside Pakistan
Offences & Nature (false information, false certificates, damage to information system etc)
VII. The Arbitration Law in Pakistan
Definitions
Appointment, number and removal of arbitrator
Award by arbitrator
Powers of court upon award (remittance, modification and setting aside of award)
Types of arbitration (with or without intervention of court)
Stay of legal proceedings in presence of arbitration agreement
VIII. Consumer’s Protection Act, 2006
Definitions
Consumer Commission (establishment, powers and functions, complaints before commission and disposal)
Provisions as to compulsory recall of goods
Duties and liabilities of provider of goods (return and refund of goods)
Offences and penalties
Contract between consumer and provider
IX. Companies Ordinance, 1984
Definitions
Types of Companies
Fundamental papers of company (Memorandum of association, articles of association, prospectus)
Transfer of shares and debentures
Management and administration (promoters, share holders, directors, chief executive, auditors)
Meeting’s and proceedings (statutory, general, annual general meeting)
Winding up (voluntary, by court)
X. Electronic Fund Transfer Act, 2007
Definitions
Payment system and their operation (designation of payment system & revocation, real time gross settlement system, governance & operation arrangement)
Payment instruments (designation, issuing and prohibition of instruments)
Clearing and other obligations
Supervisory Control of state bank
Documentation of transfers
Notification of error and liabilities of parties
Law relating to action before court.
SUGGESTED READINGS
Download CSS Mercantile Law Past Papers Download CSS Mercantile Law Books
Criminology CSS Syllabus:
Section-I (25 Marks)
I. Introduction
Basic concepts used in understanding crime, criminality and criminal behaviour.
II. Understanding Criminology
Definition, meaning and scope of criminology; Criminology and criminal law; Crime as social problem; Deviance, Sin Vice, Evil, Norms, Values; Security (Physical, Social, Economic)
III. Crime and Criminals
Occasional criminals, Habitual criminals, Professional criminals, White-collar crime, Organized crime, corporate crimes.
IV. Crime and Criminality: Theoretical Perspectives
Early explanation of criminal behavior
Biological Theories; Psychological Theories; Sociological Theories.
Social Disorganization theory
Strain theory
Social Control theory
Learning theory
Labelling Theory
Islamic perspective on deviance and crime.
Section-II (25 Marks)
V. Juvenile Delinquency
Meaning, definitions (Behavioral Vs Legal), Juvenile delinquent Vs status offender, Official statistics of juvenile delinquency
VI. Juvenile Justice System
Role of police
Juvenile court process:
pretrial, trial and sentencing
Role of prosecutor, defense counsel, juvenile judge, juvenile probation officer
Juvenile correctional institutions; probation and non-punitive alternatives
VII. The Criminal Justice System:
Police and its role
Trial and Conviction of Offenders
Agencies: formal and informal
Criminal courts: procedures and problems
Role of prosecutors
Prisons, Probation and Parole
VIII. Punitive and Reformative Treatment of Criminals
Corporal punishment, Imprisonment, Rehabilitation of criminals.
Section-III (25 Marks)
IX. Criminal Investigation
Principles of criminal investigation, Manual of preliminary investigation, Intelligence operations, Data base investigation, Electronic investigation, Forensic Investigation
X. Techniques of Investigations
Gathering information from persons, Interviewing and interrogation techniques, Criminal investigation analysis,
XI. Legal and Ethical Guidelines for Investigators
Stop and frisk operations, Arrest procedures, Search and seizure.
XII. International Policing and Criminal Justice Monitoring Organizations
UNAFEI, INTERPOL, EUROPOL, UNODC, UNICEF, IPA, etc.
Section-IV (25 Marks)
XIII. Modern Concepts in Contemporary Criminology
Terrorism, Radicalism and War on Terror
Media’s representation of Crime and the Criminal Justice System
Modern Law Enforcement and Crime Prevention
Intelligence-led Policing
Community Policing
Private Public Partnership
Gender and Crime in Urban and Rural Pakistan
Crime and Urbanization, Organized Crime and White-Collar Crime
Human Rights Abuses and Protection, especially of Children; Women and
Minorities; The role of civil society and NGOs
Money-laundering
Cyber Crime
Role of NAB, FIA, ANF
Suggested Websites
10. International Society of Criminology (ICS):
11. American Society of Criminology (ASC):
12. British Society of Criminology (BSC):
13. European Society of Criminology (ESC):
14. International Police Executive Symposium (IPES);
15. Asian Criminological Society (ACS):
16. Asian Association of Police Studies (AAPS):
17. Campbell Library:
18. UNAFEI (Japan):
19. Pakistan Society of Criminology (PSC):
20. South Asian Society of Criminology and Victimology (SASCV):
Download Criminology Past Papers Download Criminology Books
Philosophy CSS Syllabus:
I. Introduction:
Definition, Nature and Scope of Philosophy
II. Philosophical Methods:
Socratic Method (Socrates); Inductive Method (Bacon, Mill); Deductive Method (Aristotle, Descartes); Dialectical Method (Hegel); Fallibilistic Method (Popper)
III. Epistemology: Rationalism (Plato, Descartes, Spinoza); Empiricism (Locke, Berkeley, Hume); Transcendentalism (Kant); Intuitionism (Bergson)
IV. Ontology: Idealism (Plato, Berkeley); Representative Realism (Locke); Historical and Dialectical Materialism (Marx)
V. Ethics: What is morality? The challenge of cultural relativism; Does morality depend on religion? Psychological and ethical egoism: Virtue Ethics (Aristotle);
Moral Absolutism (Kant), Utilitarianism (J.S. Mill); Social Contract Theory (Hobbes, Rawls).
VI. Muslim Thinkers: Al-Farabi, Ibn Sina, Al-Ghazali, Ibn Rushid, Ibn Khaldun, Shah Waliullah, Muhammad Iqbal.
VII. Contemporary Philosophical Movements:
Existentialism (Heidegger, Sartre); Pragmatism (Peirce, James, Dewey); Neo-pragmatism (Rorty); Postmodernism (Lyotard, Foucault, Derrida)
Download Philosophy Past Papers Download Philosophy Books
Group-VII: (To select one subject of 100 marks only)
1. JOURNALISM and MASS COMMUNICATION CSS Syllabus
I. Introduction to Mass Communication
Concept – Definitions, Need/Importance/Purposes, Types of Communication, Process of Communication, Basic Models.
Functions of a model, Evaluation of a model
Basic models in Mass Communication: –
o Lasswell’s Model (1948)
o Shannon-Weaver model (1948)
o Osgood,s model (1954)
o Schramm’s model (1954)
o Newcomb’s symmetry theory (1953)
o Westley-McLean’s model (1976)
o Gerbner model (1956)
II. Mass Communication Theories
Normative theories of the press: Schramm’s four theories and criticism on these theories
Media as agents of power
The Spiral of silence
Media Usage and gratifications
Media hegemony
Diffusion of innovations
Powerful effects model: hypodermic needle, magic bullet theory.
Moderate effects model: two-step and multi-step flow of communication.
Powerful media revisited: Marshal McLuhan’s media determinism
III. Global / International Communication
The Historical Context of International Communication
Globalization, technology, and the mass media
Communication and Cultural imperialism
Communication Flow in Global Media: Imbalance in the flow of information between North and South
McBride commission and its recommendations.
International Communication in the Internet Age: the new social media and its effects on developing world
IV. Media and Society
Mass media and social change
Media as a social system: The balance between interrelation and interdependence
Media freedom and its role for democracy,
The functional approach to mass media: four social functions of the media
Media as an awareness agent
Mass media and social representation
V. Mass Media in Pakistan:
Media system in Pakistan: historical, chronological, and analytical review
The system of journalism and the media system
Employer-employee relations in Pakistani media
Government-press relations
Press in Pakistan: The newspaper industry, from mission to the market
Electronic media: from total dependence to enormous power
The new 24/7 television: uses and abuses
The new radio: potential for change and the present performance.
The question of freedom and responsibility
VI. Development Support Communication
Theories of development support communication with specific focus on the developing world
The dominant paradigm of development: historical, analytical perspective
The Alternative paradigm of development
Small is beautiful: community development as a snowball effect.
Globalization vs Localization
Glocalization
Social Marketing: how to infuse new ideas into a developing population
VII. Public Relations:
Concept of Public Relations
Historical development of public relations: from press agentry to PR
Public relation in Pakistan
Ministry of information
Press Information Department (PID)
Public relations and publicity
PR as a tool for governance
Private PR agencies and their structure
Basic methods of PR: press release, press note, press conference
PR Ethics
VIII. Media Laws and Ethics:
History of Media Laws in Pakistan
Development of media regulations from British colonial era to independent Pakistan
Libel, Defamation and relevant portions of PPC
PPO, RPPPO
PEMRA: establishment, development, and operational mechanisms
Press Council of Pakistan (PCP)
Citizens Media Commission: need, present status, and reasons for inactivity
Press Code of Ethics
Inability of the media to develop a code of ethics as an institution
The media’s quest for freedom and its inability to self regulate.
SUGGESTED READINGS
Download Journalism and Mass Communication Past Papers Download Journalism and Mass Communication Books
CSS Psychology Syllabus:
I. Nature and Scope of Psychology: Definition and scope, Psychology as a Science, Schools, Perspectives, and Models of Psychology, Recent Trends
II. Biological Basis of Behaviour: Nervous System, Neuron and its function, Central and Peripheral Nervous System, Endocrine System
III. Sensation and Perception: Sensory process, Perception, Gestalt Principles, Binocular and Monocular cues, Illusions and Extra Sensory Perception, Determinants of Perception
IV. Learning and Memory: Nature and Forms of Learning, Types of learning: Classical and Operant Conditioning, Reinforcement, Extinction, Discrimination, Punishment,
Observational Learning, Theories of Learning, Types of Memory, Process of Memory, Forgetting, Theories of Memory
V. Motivation and Emotion: Homeostasis, Factors affecting Motivation, Biogenic and Social Motives, Measurement of Human Motivation, Theories of Motivation, Emotions, Types of Emotions, Physiological changes in Emotion, Theories of Emotions.
VI. Psychological Assessment: Attributes of Psychological Measures, Validity, Reliability, Item Analysis, Norms, Modern Test Theory, Selection and Training, Educational and Clinical Assessment, Ethical and Legal Issues in Assessment.
VII. Personality: Determinants of Personality, Factors in Development of Personality, Theoretical Perspectives, Personality Assessment and Techniques, Cross-Cultural Issues.
VIII. Intelligence: Theories of Intelligence, Types of intelligence (IQ, EQ), Assessing Intelligence
IX. Social Influence and Group Dynamics: Social Facilitation, Attribution, Conformity, Obedience, Altruism, Attitudes, Social Norms.
X. Developmental Psychology: Physical, Cognitive, Social and Emotional development in Childhood, Adolescence, Adulthood and Old Age
XI. Abnormal and Clinical Psychology: Concept and causes of Abnormality, Clinical Assessment and Intervention, Different disorders such as Schizophrenia, Mood disorder, Anxiety disorder, Personality disorder, etc. Psychological treatment including different Therapeutic instructions.
XII. Organizational/Industrial Psychology: Leadership styles, Decision making, Work motivation, Organizational Culture, Stress and Conflict at Work and its Management, Organizational Socialization, Job related Attitude, Sexual Harassment, Glass Ceiling, Human Computer interaction.
XIII. Health Psychology: Beliefs and Behaviour, Models of Health Psychology, Assessment and Intervention, Models of Stress, Chronic and Terminal Illness, Role of Social Support.
XIV. Forensic Psychology: Psychology and Law, Investigation, Confession, Eyewitness Testimony, Working with Offenders, Juvenile Delinquents, Drug Addicts, Sex Offenders etc.
Download Psychology Past Papers Download Psychology Books
CSS Geography Syllabus:
Part –I (Marks 50)
Physical Geography
I. Factors controlling landform development; endogenic and exogenic forces; origin and evolution of the earth’s crust; physical conditions of the earth’s interior; geosynclines; continental drift; isostasy; sea-floor spreading; plate tectonics; mountain building;
volcanicity; earthquakes; concepts of geomorphic cycles; landforms associated with fluvial, arid, glacial, coastal and Karst cycle; groundwater.
II. Elements and Factors of climate, structure and composition of atmosphere, insolation, temperature, Pressure belts of the world; Heat budget of the earth; Atmospheric circulation: planetary, monsoon and local winds; Air masses and Fronts; Hydrological
cycle; Types of condensation and precipitation; Factors of global distribution of precipitation.
III. Origin of oceans and seas, Characteristic features of the ocean basins, temperature, salinity distribution cause and effects, Ocean floor deposits, their characteristics and classification, Ocean circulation, Waves, currents and tides, their nature, causes and effects.
IV. Factors of climate and Environmental change. Transformation of nature by man; environmental degradation and conservation; Nature and Types of pollution. Problems caused by pollution, Global Warming, Global Environment Patterns, Environmental Hazards and Risk Management.
Part –II (Marks 50)
Human Geography
V. Origin and Diffusion of Culture, Geographic patterns of culture, Classification of Languages, World Distribution of Languages, Indo-European Languages, Origins of Religions, Diffusion of Religions, Global Distribution, Regional conflicts, Ethnicities and Nationalities, Ethnic Conflicts, Ethnic Diversity in the World, Factors of Ethnic Cleansing, Ethnic Cleansing in the World, Development Indicators, Economic Indicators, Social Indicators, Health Indicators, Development through Trade, Impacts of development Indicators.
VI. Factors effecting Agriculture, Subsistence Agriculture and population growth, Commercial Agriculture and Market Forces, Sustainable Agriculture, Types and Distribution of Agriculture, Factors of Industrial locations, The Industrial Revolution,
Industrial Theories, Distribution of Industries and Industrial Estates, Renewable Resources, Recycling Resources, Sustainable resources.
VII. Factors of Population Growth, Components of Change, Population Structure, The Demographic Transition, World distribution of Population, Over and under Population
threats and their consequences, Models of Internal Structure of Cities, World Urban Patterns, Settlement Theories, Patterns and Problems within urban areas.
VIII. Politics, Geography and Political Geography, State as a Politico-Territorial Phenomenon, State, Nation and the Nation-State, World Politics and International Relations, Geopolitics of uneven Development and Globalization of Capital,
Geography of Tourism and Recreation, The demand for tourism and recreation, The supply for tourism and recreation, The impact of tourism and recreation: (Socioeconomic
impacts, Physical-environmental impacts), Global patterns in health and diseases, Models in medical geography, Recent issues and developments.
Download Geography Past Papers Download Geography Books
CSS Sociology Syllabus:
I. General Sociology
1. Individual: Sociability or the sociality of man.
2. Culture: Meaning and Characteristics (Culture is variable, learnt, social, shared, transmissive, dynamic and adaptive), types (Material, Non –material), functions (transfer of knowledge, define situation, provide behaviour pattern, moulds personality) and elements of culture (norms, values, beliefs, sanctions, customs).
Culture and Socialization; formal and non-formal socialization, transmission of culture, cultural relativism. Sub-cultures. Ethnocentrism and xenocentrism, Cultural lag, High culture and popular culture. Multiculturalism, assimilation, and acculturation.
3. Society: Meaning and characteristics. Community; meaning and characteristics. Individual and society. Relationship between individual and society. Two main theories regarding the relationship of man and society
(i) the social contact theory and
(ii) the organismic theory. Social and cultural evolution of society (Hunting and Gathering Society, Herding and Advance Herding Society, Horticultural Society, Agrarian Society, Industrial Society, Post modern Society).
4. Social Interaction: Caste and classes, Forms of social classes, Feudal system in Pakistan, Social Mobility-nature of social mobility and its determinants in Pakistani society, Culture of poverty.
5. Social Control: Mechanisms of social control-formal and informal means of social control, Anomie, Alienation and social Integration-Means of social integration in Pakistani Society.
6. Social and Cultural Change and Social Policy: Processes of Social and Cultural Change-discovery, Inhibitions to social and cultural change in Pakistan, Social planning and directed social and cultural change, Effect of Industrialization,
Urbanization, Modernization and Modern Means of Communication on Social Change.
7. Public Opinion: Formation of public opinion, concept of opinion leader, characteristics of opinion leadership.
8. Community: The rural community, Traditional Characteristics of rural life, The urban community, Rural – Urban convergence, Urbanism, Future of cities in Pakistan.
9. Social Institutions: The nature and genesis of institutions, The process of institutionalization, Functions of Social Institutions: Family, Religion, Education, Economy and Politics.
10. Social Problems in Pakistan: High population growth rate, Rural –urban migration. Issues of technical/vocational training, Deviance and street crime, Unemployment, illiteracy and School drop out, Smuggling, Prostitution, Poverty, Drug Addiction, Child Labour and Abuse, Bonded Labour, Social customs and Traditions affecting Women in Pakistan, Violence Against Women and Domestic Violence, Issues concerning the Elderly in Pakistan.
II. Sociological Theory:
Three sociological perspectives: Structural Functionalism, Symbolic interactions and Conflict. Theorists: Ibn-i-Khaldun, Spencer, August Comte, Emile Dukheim, Max Weber, Karl Marx, Parson.
III. Methods of Sociological Research:
Scientific Method, Steps in research, Types of Questionnaire Research Design, Surveys, Observation and Case Studies.
Download Sociology Past Papers Download Sociology Books
CSS Anthropology Syllabus:
I. Anthropology
Definition of anthropology, its historical development and recent trends
II. Social Anthropology
Definition of culture, its characteristics and functions
Relationship of anthropology with other social sciences
Sub fields of anthropology:
a) Biological Anthropology,
b) Archaeology,
c) Linguistic Anthropology
d) Socio-Cultural Anthropology
Institution of Family and Marriage
(Definitions, types, structures, functions, family organization)
Kinship and Social Organization
(Definitions, types, functions, kinship terminology etc)
Economic Organization:
(Definitions, evolution, substantivism versus formalism, reciprocity, production, consumption, distribution, barter and primitive economic systems)
Political Organization:
(Definitions, evolution of political system, characteristics of (band, tribal, chiefdom and state societies), theories of the origin of state societies (internal conflict theories, external conflict theories, population and irrigation theories, institutionalization of leadership and the emergence of state, system theories), origin of civilization, the politics of identity, ethnicity and ethnic relations, nationalism, modernism, post-modernism etc.
Religion:
(Definitions, evolution of primitive religions, functions of religion, comparison of devine religions and other world religions such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism etc)
Contemporary Human Problems:
Poverty, social inequality, political instability, population problems, ethnic violence and terrorism etc.
III. Urban Anthropology Rural-urban migration, expansion of cities, major environmental issues, sanitation problems, urbanization and development, establishment of slums and squatter settlements, refugees, yankees, betties, gypsies, wars and conflict, conversion of power from feudal to industrialists, institutionalization, education system, and change in the mode of production (agriculture to capitalists), poverty (theories and remedies), management of city life (psychological, cultural, economic, political, religious, physical, environmental, ecological, demographical, lingual etc.), Karl Marx and conflict theory, problems created by the mechanization and automation.
IV. Socio-Cultural Change
Definitions, difference between social and cultural change, various dimension of cultural change, barriers to cultural change including (culture, psychological and political), internal dynamics for change, external dynamics for change, population incease and change, diffusion of innovations, socio-religious barriers in accepting the innovations and new ideas, media and cultural change, dynamics of change in Pakistan (Trends and prospects)
V. Ethnicity and Race
Theories related to ethnicity and race, ethnicity and racism, nations and nationality, ethnic conflict, degree of social variation, rank societies, caste and class societies and social stratification etc.
VI. Anthropological Theories
Contributors: (Edward Burnett Taylor, Lewis Henry Morgan, James Frazer, Karl Marx, Edmund Leach, Franz Boas, Margaret Mead, Ruth Benedict, Alfred L. Krobber, Alfred Reginald Radcliffe-Brown, Bronislaw Kasper Malinowski, Clifford Geertz, Talal Asad, Akbar S. Ahamd, Ibn Khaldun, Shah Walliullah)
Classical Theories: (Degenerations, Evolutionism, Neo-Evolutionism, Diffusions)
Modern Theories: (Functionalism, Structural-functionalism, Class struggle, Structuralism, Historical Particularism, Feminism, Culture and personality)
Current Trends in Anthropological Thoughts: (Post Modernism, Romanticism, Poetics and Politics of Ethnography)
VII. Anthropological Research Methods
Meaning, definition, types and aims of anthropological research
Qualitative and Quantitative research
Purpose of research, research question, variables, hypothesis, research objective(s), research design, sampling, field data collection, tools of data collection (questionnaire, interview, participant observation), data classification, data analysis, and reporting.


Download Anthropology Past Papers