JOURNALISM and MASS COMMUNICATION CSS Syllabus
PAPER: JOURNALISM & MASS COMMUNICATION (100 MARKS)
I. Introduction to Mass Communication
Concept – Definitions, Need/Importance/Purposes, Types of Communication, Process of Communication, Basic Models.
Functions of a model, Evaluation of a model
Basic models in Mass Communication: –
o Lasswell’s Model (1948)
o Shannon-Weaver model (1948)
o Osgood,s model (1954)
o Schramm’s model (1954)
o Newcomb’s symmetry theory (1953)
o Westley-McLean’s model (1976)
o Gerbner model (1956)
II. Mass Communication Theories
Normative theories of the press: Schramm’s four theories and criticism on these theories
Media as agents of power
The Spiral of silence
Media Usage and gratifications
Media hegemony
Diffusion of innovations
Powerful effects model: hypodermic needle, magic bullet theory.
Moderate effects model: two-step and multi-step flow of communication.
Powerful media revisited: Marshal McLuhan’s media determinism
III. Global / International Communication
The Historical Context of International Communication
Globalization, technology, and the mass media
Communication and Cultural imperialism
Communication Flow in Global Media: Imbalance in the flow of information between North and South
McBride commission and its recommendations.
International Communication in the Internet Age: the new social media and its effects on developing world
IV. Media and Society
Mass media and social change
Media as a social system: The balance between interrelation and interdependence
Media freedom and its role for democracy,
The functional approach to mass media: four social functions of the media
Media as an awareness agent
Mass media and social representation
V. Mass Media in Pakistan:
Media system in Pakistan: historical, chronological, and analytical review
The system of journalism and the media system
Employer-employee relations in Pakistani media
Government-press relations
Press in Pakistan: The newspaper industry, from mission to the market
Electronic media: from total dependence to enormous power
The new 24/7 television: uses and abuses
The new radio: potential for change and the present performance.
The question of freedom and responsibility
VI. Development Support Communication
Theories of development support communication with specific focus on the developing world
The dominant paradigm of development: historical, analytical perspective
The Alternative paradigm of development
Small is beautiful: community development as a snowball effect.
Globalization vs Localization
Glocalization
Social Marketing: how to infuse new ideas into a developing population
VII. Public Relations:
Concept of Public Relations
Historical development of public relations: from press agentry to PR
Public relation in Pakistan
Ministry of information
Press Information Department (PID)
Public relations and publicity
PR as a tool for governance
Private PR agencies and their structure
Basic methods of PR: press release, press note, press conference
PR Ethics
VIII. Media Laws and Ethics:
History of Media Laws in Pakistan
Development of media regulations from British colonial era to independent Pakistan
Libel, Defamation and relevant portions of PPC
PPO, RPPPO
PEMRA: establishment, development, and operational mechanisms
Press Council of Pakistan (PCP)
Citizens Media Commission: need, present status, and reasons for inactivity
Press Code of Ethics
Inability of the media to develop a code of ethics as an institution
The media’s quest for freedom and its inability to self regulate.
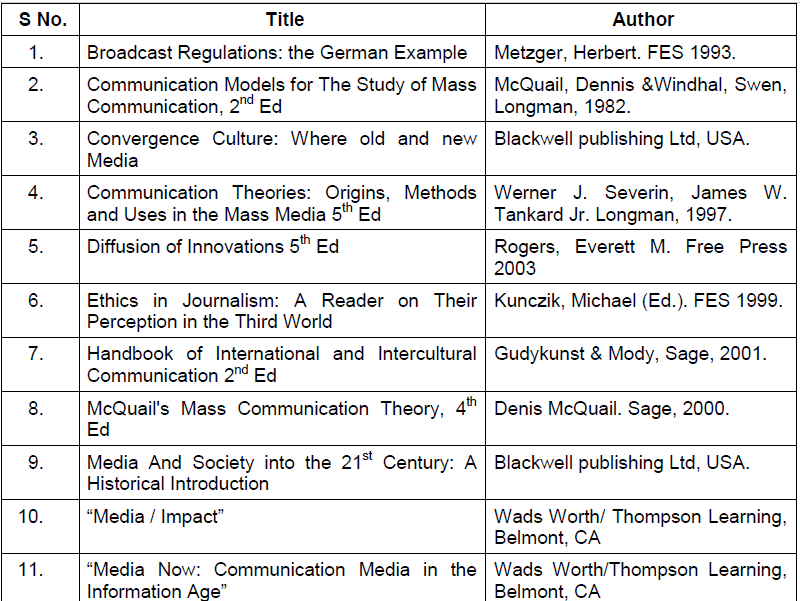
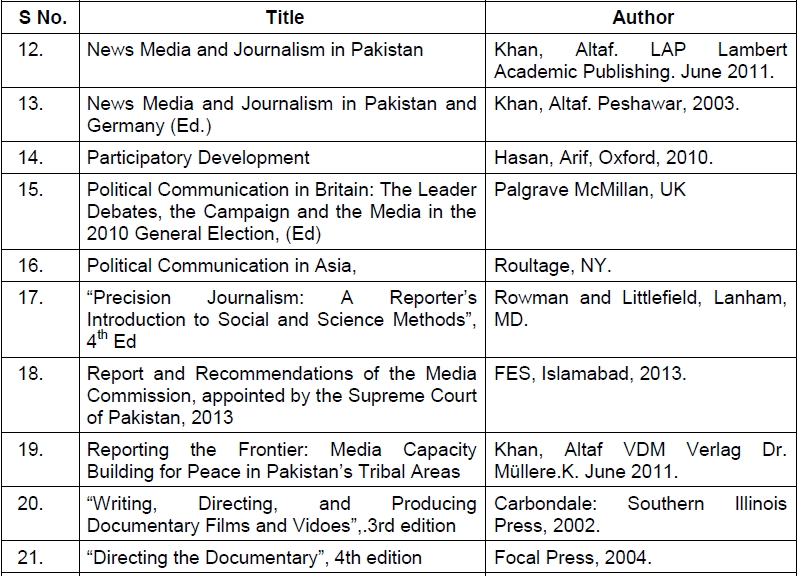
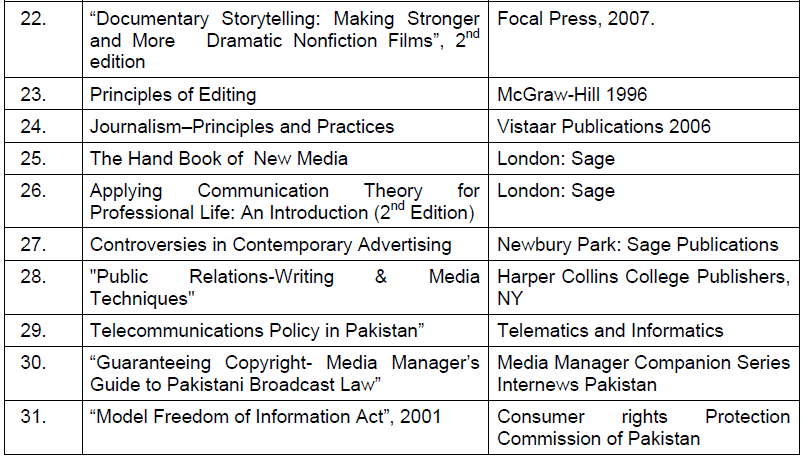
SUGGESTED READINGS
Download Journalism and Mass Communication Past Papers Download Journalism and Mass Communication Books Download Full CSS Syllabus